
Back أسيتانيليد Arabic استانیلید AZB অ্যাসিটানিলাইড Bengali/Bangla Acetanilid Czech Ακετανιλίδιο Greek Acetanilide English Acetanilido EO Acetanilida Spanish Azetanilida EU استانیلید FA
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
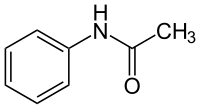
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Acetanilid | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C8H9NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farbloser Feststoff mit charakteristischem Geruch[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 135,17 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
1,21 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
305 °C[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| pKS-Wert |
0,5 (25 °C)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamische Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔHf0 |
−209,4 kJ·mol−1 (Feststoff)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
Acetanilid ist ein Derivat sowohl von Anilin als auch von Essigsäure und wurde 1843 von Charles Frédéric Gerhardt durch Einwirkung von Acetylchlorid auf Anilin entdeckt.
- ↑ Eintrag zu ACETANILID in der CosIng-Datenbank der EU-Kommission, abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2021.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Eintrag zu Acetanilid in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 1. Februar 2016. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ W. M. Haynes (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 97. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2016), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton FL, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases, S. 5-88.
- ↑ Hermann P. T. Ammon, Manfred Schubert-Zsilavecz (Hrsg.): Hunnius. Pharmazeutisches Wörterbuch. 11. Auflage. de Gruyter, Berlin/Boston 2014, ISBN 978-3-11-030990-4, S. 12.
- ↑ W. M. Haynes (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 97. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2016), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, S. 5-3.
