Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Akad
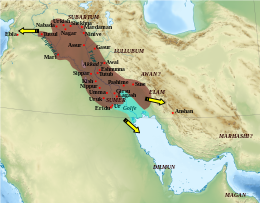
Akkad (/ˈækæd/) atau Agade (cuneiform: 𒌵𒆠 URIKI) adalah nama dari sebuah kota Mesopotamia dan wilayah sekitarnya.[1] Akkad adalah ibukota Kekaisaran Akkadia, yang merupakan pasukan politik dominan di Mesopotamia pada periode sekitar 150 tahun pada paruh ketiga terakhir dari milenium ke-3 SM.
Lokasinya tidak diketahui, meskipun terdapat sejumlah situs kandidat, kebanyakan berada di timur Tigris, yang terbentang antara kota-kota modern Samarra dan Baghdad.[2]
- ^ Foster (2013): "Akkad was originally the name of an area and city near the confluence of the Diyala and Tigris rivers in Mesopotamia (Adams 1965; Weiss 1997). The meaning of the word is unknown. After it became the seat of the Sargonic Dynasty around 2300 bce, Akkad as a territory expanded to mean northern Babylonia, from north of Nippur to Sippar. The city of the same name is first attested in the late Early Dynastic period, became an imperial capital in the Sargonic period, and was still occupied in the second millennium. By the mid‐first millennium the city's cults had been transferred elsewhere and the former capital was a famous ruin. In modern scholarship, the city is often distinguished from the region by calling it Agade. Its location has not been identified."
- ^ "Akkade may thus be one of the many large tells on the confluence of the Adheim River with the Tigris" (Sallaberger, and Westenholz 1999, p. 32.
Previous Page Next Page


