
Back أميكاسين Arabic آمیکاسین AZB Амикацин Bulgarian Amikacina Catalan Amicacin CY Amikacin German Amikacina Spanish Amikazina EU آمیکاسین FA Amikasiini Finnish
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Amikin, Amiglyde-V, Arikayce, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682661 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, intravenous, inhalation |
| Drug class | Aminoglycoside |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >90%[8] |
| Protein binding | 0–11% |
| Metabolism | Mostly unmetabolized |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.653 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
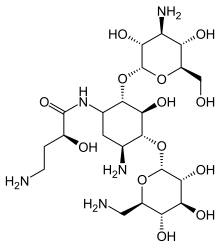
| Formula | C22H43N5O13 |
| Molar mass | 585.608 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Amikacin is an antibiotic medication used for a number of bacterial infections.[9] This includes joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections.[9] It is also used for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.[10] It is used by injection into a vein using an IV or into a muscle.[9]
Amikacin, like other aminoglycoside antibiotics, can cause hearing loss, balance problems, and kidney problems.[9] Other side effects include paralysis, resulting in the inability to breathe.[9] If used during pregnancy it may cause permanent deafness in the baby.[9][1] Amikacin works by blocking the function of the bacteria's 30S ribosomal subunit, making it unable to produce proteins.[9]
Amikacin was patented in 1971, and came into commercial use in 1976.[11][12] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[13] It is derived from kanamycin.[9]
- ^ a b "Amikacin Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 2 December 2019. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new generic medicines and biosimilar medicines, 2017". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "Amikacin 250 mg/ml Injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 16 September 2015. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Arikayce FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Arikayce liposomal EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 21 July 2020. Retrieved 4 March 2023.
- ^ "Arikayce liposomal Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
plumbwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h "Amikacin Sulfate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. p. 137. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 507. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. 2009. p. 56. ISBN 9780191039621. Archived from the original on 24 November 2015.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.