
Back بيتا لاكتاماز Arabic Beta laktamazlar AZ Beta-lactamasa Catalan Beta-laktamáza Czech Betalactamase Danish Β-Lactamasen German Betalactamasa Spanish Beta-laktamasa EU بتالاکتاماز FA Beetalaktamaasi Finnish
| Serine beta-lactamase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Structure of Streptomyces albus beta-lactamase | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | β-lactamase domain | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00144 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0013 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001466 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PS00146 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 56601 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Metallo-beta-lactamase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Metallo-beta-lactamase L1 homotetramer, Stenotrophomonas | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | ? | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00753 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0381 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001279 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| β-lactamase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
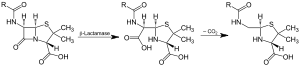 Action of β-lactamase and decarboxylation of the intermediate | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.5.2.6 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9073-60-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||


Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.
Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.[1]
- ^ Neu HC (June 1969). "Effect of beta-lactamase location in Escherichia coli on penicillin synergy". Applied Microbiology. 17 (6): 783–6. doi:10.1128/AEM.17.6.783-786.1969. PMC 377810. PMID 4894721.