
Back كرياتينين Arabic كرياتينين ARY کراتینین AZB Креатинин Bulgarian ক্রিয়েটিনিন Bengali/Bangla Kreatinin BS Creatinina Catalan Kreatinin German Κρεατινίνη Greek Kreatinino EO
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
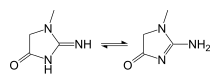
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one[citation needed] | |
| Other names
2-Amino-1-methylimidazol-4-ol[citation needed]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 112061 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.424 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Creatinine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1789 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7N3O | |
| Molar mass | 113.120 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Density | 1.09 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K)[1] (decomposes) |
| 1 part per 12[1]
90 mg/mL at 20°C[2] | |
| log P | -1.76 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.309 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 1.688 |
| Isoelectric point | 11.19 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
138.1 J K−1 mol−1 (at 23.4 °C) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
167.4 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−240.81–239.05 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.33539–2.33367 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Creatinine (/kriˈætɪnɪn, -ˌniːn/; from Ancient Greek κρέας (kréas) 'flesh') is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).[3][4]
- ^ a b Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2571
- ^ "Creatinine, anhydrous - CAS 60-27-5". Scbt.com. Archived from the original on 2016-10-22. Retrieved 2016-10-21.
- ^ "Creatinine tests - Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Archived from the original on 2022-06-05.
- ^ Lewis SL, Bucher L, Heitkemper MM, Harding MM, Kwong J, Roberts D (September 2016). Medical-surgical nursing : assessment and management of clinical problems (10th ed.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1025. ISBN 978-0-323-37143-8. OCLC 228373703.
