Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
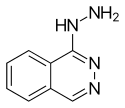
Hydralazine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Apresoline, BiDil, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682246 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 26–50% |
| Protein binding | 85–90% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Onset of action | 5 to 30 min[2] |
| Elimination half-life | 2–8 hours, 7–16 hours (renal impairment) |
| Duration of action | 2 to 6 hrs[2] |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.528 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H8N4 |
| Molar mass | 160.180 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Hydralazine, sold under the brand name Apresoline among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure.[2] This includes high blood pressure in pregnancy and very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms.[3] It has been found to be particularly useful in heart failure, together with isosorbide dinitrate, for treatment of people of African descent.[2] It is given by mouth or by injection into a vein.[3] Effects usually begin around 15 minutes and last up to six hours.[2]
Common side effects include headache and fast heart rate.[2] It is not recommended in people with coronary artery disease or in those with rheumatic heart disease that affects the mitral valve.[2] In those with kidney disease a low dose is recommended.[3] Hydralazine is in the vasodilator family of medications, so it is believed to work by causing the dilation of blood vessels.[2]
Hydralazine was discovered while scientists at Ciba were looking for a treatment for malaria.[4] It was patented in 1949.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] In 2022, it was the 121st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5 million prescriptions.[7][8]
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new generic medicines and biosimilar medicines, 2017". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Hydralazine Hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. p. 280. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ Wermuth CG (2 May 2011). The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. p. 12. ISBN 9780080568775. Archived from the original on 26 February 2017.
- ^ Progress in Drug Research/Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung/Progrés des recherches pharmaceutiques. Birkhäuser. 2013. p. 206. ISBN 9783034870948. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Hydralazine Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
Previous Page Next Page


