Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
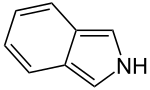
Isoindole
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-Isoindole[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7N | |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In organic chemistry and heterocyclic chemistry, isoindole consists of a benzene ring fused with pyrrole.[2] The compound is an isomer of indole. Its reduced form is isoindoline. The parent isoindole is a rarely encountered in the technical literature, but substituted derivatives are useful commercially and occur naturally. Isoindoles units occur in phthalocyanines, an important family of dyes. Some alkaloids containing isoindole have been isolated and characterized.[3][4]
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 213. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Gilchrist, T. L. (1987). Heterocyclic Chemistry. Longman. ISBN 0-582-01422-0.
- ^ Heugebaert, Thomas S. A.; Roman, Bart I.; Stevens, Christian V. "Synthesis of isoindoles and related iso-condensed heteroaromatic pyrroles" Chemical Society Reviews 2012, volume 41, pp. 5626-5640. doi:10.1039/c2cs35093a
- ^ See for example: Zhang, X.; Ye, W.; Zhao, S.; Che, C. T. (2004). "Isoquinoline and isoindole alkaloids from Menispermum dauricum". Phytochemistry. 65 (7): 929–932. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2003.12.004. PMID 15081297.
Previous Page Next Page


