Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
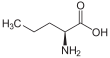
Norvaline
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Aminopentanoic acid
| |||
| Other names
2-Aminovaleric acid; α-Aminopentanoic acid; Propylglycine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.858 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 117.148 g·mol−1 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.36 (carboxyl), 9.76 (amino)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Norvaline (abbreviated as Nva) is an amino acid with the formula CH3(CH2)2CH(NH2)CO2H. The compound is a structural analog of valeric acid and also an isomer of the more common amino acid valine.[2] Like most other α-amino acids, norvaline is chiral. It is a white, water-soluble solid.
- ^ Dawson, R.M.C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.[page needed]
- ^ Merriam-Webster Retrieved 4 September 2010
Previous Page Next Page