Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Pentene
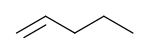 1-Pentene
| |
 cis-2-Pentene
| |
 trans-2-Pentene
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Pent-1-ene
cis-Pent-2-ene trans-Pent-2-ene | |
| Other names
amylene, n-amylene, n-pentene, beta-n-amylene, sym-methylethylethylene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.636 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10 | |
| Molar mass | 70.135 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.64 g/cm3 (1-pentene)[1] |
| Melting point | −165.2 °C (−265.4 °F; 108.0 K) (1-pentene)[1] |
| Boiling point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) (1-pentene)[1] |
| -53.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pentenes are alkenes with the chemical formula C
5H
10. Each molecule contains one double bond within its molecular structure. Six different compounds are in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched structure and whether the double bond has a cis or trans form.
- ^ a b c Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
Previous Page Next Page


