Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Silanone
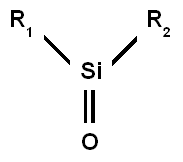
A silanone in chemistry is the silicon analogue of a ketone. The general description for this class of organic compounds is R1R2Si=O, with silicon connected to a terminal oxygen atom via a double bond and also with two organic residues (R).[1] Silanones are extremely reactive[1] and until 2013 were only detected by argon matrix isolation[2][3] or in the gas phase[4] but not isolated. A synthesis of a stable silanone was reported in 2014. Silanones are of some interest to academic research, with their reactivity being of some relevance to the double bond rule.
Silanones are unstable and favor oligomerisation to siloxanes. The reason for this instability is the weak pi bond with a small HOMO–LUMO energy gap caused by an unfavorable overlap between the p-orbitals of silicon and oxygen. A second reason for the observed instability is the strongly polarized silicon–oxygen bond, Siδ+–Oδ−.[1]
- ^ a b c Sen, S. S. (2014). "A Stable Silanone with a Three-Coordinate Silicon Atom: A Century-Long Wait is Over". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53 (34): 8820–8822. doi:10.1002/anie.201404793. PMID 24990653.
- ^ On the proposed thermal interconversion of matrix-isolated dimethylsilylene and 1-methylsilene: their reactions with oxygen atom donors Charles A. Arrington, Robert West, Josef Michl J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105 (19), pp 6176–6177 doi:10.1021/ja00357a048
- ^ Infrared spectroscopic evidence for silicon-oxygen double bonds: silanone and the silanoic and silicic acid molecules Robert Withnall, Lester Andrews J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1985, 107 (8), pp 2567–2568 doi:10.1021/ja00294a070
- ^ M. Bogey; B. Delcroix; A. Walters; J-C Guillemin (1996). "Experimentally Determined Structure of H2SiO by Rotational Spectroscopy and Isotopic Substitution". J. Mol. Spectrosc. 175 (2): 421–428. Bibcode:1996JMoSp.175..421B. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0048.
Previous Page Next Page


