Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
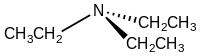
Triethylamine
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Diethylethanamine | |||
| Other names
(Triethyl)amine
Triethylamine (no longer IUPAC name[1]) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | TEA[2] | ||
| 605283 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.064 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | triethylamine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1296 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[5] | |||
| C6H15N | |||
| Molar mass | 101.193 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal | ||
| Density | 0.7255 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −114.70 °C; −174.46 °F; 158.45 K | ||
| Boiling point | 88.6 to 89.8 °C; 191.4 to 193.5 °F; 361.7 to 362.9 K | ||
| 112.4 g/L at 20 °C[3] | |||
| Solubility | miscible with organic solvents | ||
| log P | 1.647 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 6.899–8.506 kPa | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
66 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.75 (for the conjugate acid) (H2O), 9.00 (DMSO)[4] | ||
| -81.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.401 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
216.43 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−169 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4.37763 to −4.37655 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |||
| P210, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) | ||
| 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–8% | ||
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
2 ppm (8 mg/m3) (TWA), 4 ppm (17 mg/m3) (STEL) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
1425 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[7] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3)[6] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
None established[6] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
200 ppm[6] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related amines
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. Like triethanolamine and tetraethylammonium, it is often abbreviated TEA.[8][9] It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 671. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ X. Bories-Azeau, S. P. Armes, and H. J. W. van den Haak, Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2348 PDF
- ^ "MSDS - 471283". www.sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
David Evans Research Groupwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The Merck Index (11th ed.). 9582.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0633". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Triethylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Ethanolamine Compounds (MEA, DEA, TEA And Others)". Safe Cosmetics. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ^ "tetraethylammonium | Ligand page | IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY". www.guidetopharmacology.org. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
Previous Page Next Page





