Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Mathematics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Wikipedia portal for content related to Mathematics
-
Abacus, a ancient hand-operated calculating.
-
Portrait of Emmy Noether, around 1900.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). (Full article...)
Featured articles
-
Image 1Portrait by August Köhler, c. 1910, after 1627 original
Johannes Kepler (/ˈkɛplər/; German: [joˈhanəs ˈkɛplɐ, -nɛs -] ⓘ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonice Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae, influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel Somnium.
Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein.
Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, being named the father of modern optics, in particular for his Astronomiae pars optica. He also invented an improved version of the refracting telescope, the Keplerian telescope, which became the foundation of the modern refracting telescope, while also improving on the telescope design by Galileo Galilei, who mentioned Kepler's discoveries in his work. He is also known for postulating the Kepler conjecture. (Full article...) -
Image 2The title page of a 1634 version of Hues' Tractatus de globis in the collection of the Biblioteca Nacional de Portugal
Robert Hues (1553 – 24 May 1632) was an English mathematician and geographer. He attended St. Mary Hall at Oxford, and graduated in 1578. Hues became interested in geography and mathematics, and studied navigation at a school set up by Walter Raleigh. During a trip to Newfoundland, he made observations which caused him to doubt the accepted published values for variations of the compass. Between 1586 and 1588, Hues travelled with Thomas Cavendish on a circumnavigation of the globe, performing astronomical observations and taking the latitudes of places they visited. Beginning in August 1591, Hues and Cavendish again set out on another circumnavigation of the globe. During the voyage, Hues made astronomical observations in the South Atlantic, and continued his observations of the variation of the compass at various latitudes and at the Equator. Cavendish died on the journey in 1592, and Hues returned to England the following year.
In 1594, Hues published his discoveries in the Latin work Tractatus de globis et eorum usu (Treatise on Globes and Their Use) which was written to explain the use of the terrestrial and celestial globes that had been made and published by Emery Molyneux in late 1592 or early 1593, and to encourage English sailors to use practical astronomical navigation. Hues' work subsequently went into at least 12 other printings in Dutch, English, French and Latin. (Full article...) -
Image 3One of Molyneux's celestial globes, which is displayed in Middle Temple Library – from the frontispiece of the Hakluyt Society's 1889 reprint of A Learned Treatise of Globes, both Cœlestiall and Terrestriall, one of the English editions of Robert Hues' Latin work Tractatus de Globis (1594)
Emery Molyneux (/ˈɛməri ˈmɒlɪnoʊ/ EM-ər-ee MOL-in-oh; died June 1598) was an English Elizabethan maker of globes, mathematical instruments and ordnance. His terrestrial and celestial globes, first published in 1592, were the first to be made in England and the first to be made by an Englishman.
Molyneux was known as a mathematician and maker of mathematical instruments such as compasses and hourglasses. He became acquainted with many prominent men of the day, including the writer Richard Hakluyt and the mathematicians Robert Hues and Edward Wright. He also knew the explorers Thomas Cavendish, Francis Drake, Walter Raleigh and John Davis. Davis probably introduced Molyneux to his own patron, the London merchant William Sanderson, who largely financed the construction of the globes. When completed, the globes were presented to Elizabeth I. Larger globes were acquired by royalty, noblemen and academic institutions, while smaller ones were purchased as practical navigation aids for sailors and students. The globes were the first to be made in such a way that they were unaffected by the humidity at sea, and they came into general use on ships. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Logic studies valid forms of inference like modus ponens.
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.
Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to work". Premises and conclusions express propositions or claims that can be true or false. An important feature of propositions is their internal structure. For example, complex propositions are made up of simpler propositions linked by logical vocabulary like(and) or
(if...then). Simple propositions also have parts, like "Sunday" or "work" in the example. The truth of a proposition usually depends on the meanings of all of its parts. However, this is not the case for logically true propositions. They are true only because of their logical structure independent of the specific meanings of the individual parts. (Full article...)
-
Image 5Archimedes Thoughtful by Fetti (1620)
Archimedes of Syracuse (/ˌɑːrkɪˈmiːdiːz/ AR-kim-EE-deez; c. 287 – c. 212 BC) was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Regarded as the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time, Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral.
Archimedes' other mathematical achievements include deriving an approximation of pi (π), defining and investigating the Archimedean spiral, and devising a system using exponentiation for expressing very large numbers. He was also one of the first to apply mathematics to physical phenomena, working on statics and hydrostatics. Archimedes' achievements in this area include a proof of the law of the lever, the widespread use of the concept of center of gravity, and the enunciation of the law of buoyancy known as Archimedes' principle. In astronomy, he made measurements of the apparent diameter of the Sun and the size of the universe. He is also credited with designing innovative machines, such as his screw pump, compound pulleys, and defensive war machines to protect his native Syracuse from invasion. (Full article...) -
Image 6A stamp of Zhang Heng issued by China Post in 1955
Zhang Heng (Chinese: 張衡; AD 78–139), formerly romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mathematician, seismologist, hydraulic engineer, inventor, geographer, cartographer, ethnographer, artist, poet, philosopher, politician, and literary scholar.
Zhang Heng began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stance on historical and calendrical issues led to his becoming a controversial figure, preventing him from rising to the status of Grand Historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian Kingdom in present-day Hebei. Zhang returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. (Full article...) -
Image 7Damage from Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Actuaries need to estimate long-term levels of such damage in order to accurately price property insurance, set appropriate reserves, and design appropriate reinsurance and capital management strategies.
An actuary is a professional with advanced mathematical skills who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require asset management, liability management, and valuation skills. Actuaries provide assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms. The name of the corresponding academic discipline is actuarial science.
While the concept of insurance dates to antiquity, the concepts needed to scientifically measure and mitigate risks have their origins in the 17th century studies of probability and annuities. Actuaries of the 21st century require analytical skills, business knowledge, and an understanding of human behavior and information systems to design programs that manage risk, by determining if the implementation of strategies proposed for mitigating potential risks, does not exceed the expected cost of those risks actualized. The steps needed to become an actuary, including education and licensing, are specific to a given country, with various additional requirements applied by regional administrative units; however, almost all processes impart universal principles of risk assessment, statistical analysis, and risk mitigation, involving rigorously structured training and examination schedules, taking many years to complete. (Full article...) -
Image 8In algebraic geometry and theoretical physics, mirror symmetry is a relationship between geometric objects called Calabi–Yau manifolds. The term refers to a situation where two Calabi–Yau manifolds look very different geometrically but are nevertheless equivalent when employed as extra dimensions of string theory.
Early cases of mirror symmetry were discovered by physicists. Mathematicians became interested in this relationship around 1990 when Philip Candelas, Xenia de la Ossa, Paul Green, and Linda Parkes showed that it could be used as a tool in enumerative geometry, a branch of mathematics concerned with counting the number of solutions to geometric questions. Candelas and his collaborators showed that mirror symmetry could be used to count rational curves on a Calabi–Yau manifold, thus solving a longstanding problem. Although the original approach to mirror symmetry was based on physical ideas that were not understood in a mathematically precise way, some of its mathematical predictions have since been proven rigorously. (Full article...) -
Image 9

The regular triangular tiling of the plane, whose symmetries are described by the affine symmetric group S̃3
The affine symmetric groups are a family of mathematical structures that describe the symmetries of the number line and the regular triangular tiling of the plane, as well as related higher-dimensional objects. In addition to this geometric description, the affine symmetric groups may be defined in other ways: as collections of permutations (rearrangements) of the integers (..., −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, ...) that are periodic in a certain sense, or in purely algebraic terms as a group with certain generators and relations. They are studied in combinatorics and representation theory.
A finite symmetric group consists of all permutations of a finite set. Each affine symmetric group is an infinite extension of a finite symmetric group. Many important combinatorial properties of the finite symmetric groups can be extended to the corresponding affine symmetric groups. Permutation statistics such as descents and inversions can be defined in the affine case. As in the finite case, the natural combinatorial definitions for these statistics also have a geometric interpretation. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Josiah Willard Gibbs (/ɡɪbz/; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American scientist who made significant theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynamics was instrumental in transforming physical chemistry into a rigorous deductive science. Together with James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann, he created statistical mechanics (a term that he coined), explaining the laws of thermodynamics as consequences of the statistical properties of ensembles of the possible states of a physical system composed of many particles. Gibbs also worked on the application of Maxwell's equations to problems in physical optics. As a mathematician, he created modern vector calculus (independently of the British scientist Oliver Heaviside, who carried out similar work during the same period) and described the Gibbs phenomenon in the theory of Fourier analysis.
In 1863, Yale University awarded Gibbs the first American doctorate in engineering. After a three-year sojourn in Europe, Gibbs spent the rest of his career at Yale, where he was a professor of mathematical physics from 1871 until his death in 1903. Working in relative isolation, he became the earliest theoretical scientist in the United States to earn an international reputation and was praised by Albert Einstein as "the greatest mind in American history". In 1901, Gibbs received what was then considered the highest honor awarded by the international scientific community, the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London, "for his contributions to mathematical physics". (Full article...) -
Image 11Portrait by Jakob Emanuel Handmann, 1753
Leonhard Euler (/ˈɔɪlər/ OY-lər; German: [ˈleːɔnhaʁt ˈʔɔʏlɐ] ⓘ, Swiss Standard German: [ˈleɔnhard ˈɔʏlər]; 15 April 1707 – 18 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia.
Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter(lowercase pi) to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, as well as first using the notation
for the value of a function, the letter
to express the imaginary unit
, the Greek letter
(capital sigma) to express summations, the Greek letter
(capital delta) for finite differences, and lowercase letters to represent the sides of a triangle while representing the angles as capital letters. He gave the current definition of the constant
, the base of the natural logarithm, now known as Euler's number. Euler made contributions to applied mathematics and engineering, such as his study of ships which helped navigation, his three volumes on optics contributed to the design of microscopes and telescopes, and he studied the bending of beams and the critical load of columns. (Full article...)
-
Image 12

The manipulations of the Rubik's Cube form the Rubik's Cube group.
In mathematics, a group is a set with an operation that associates every pair of elements of the set to an element of the set (as does every binary operation) and satisfies the following constraints: the operation is associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element.
Many mathematical structures are groups endowed with other properties. For example, the integers with the addition operation form an infinite group, which is generated by a single element called (these properties characterize the integers in a unique way). (Full article...)
-
Image 13

Émile Michel Hyacinthe Lemoine (French: [emil ləmwan]; 22 November 1840 – 21 February 1912) was a French civil engineer and a mathematician, a geometer in particular. He was educated at a variety of institutions, including the Prytanée National Militaire and, most notably, the École Polytechnique. Lemoine taught as a private tutor for a short period after his graduation from the latter school.
Lemoine is best known for his proof of the existence of the Lemoine point (or the symmedian point) of a triangle. Other mathematical work includes a system he called Géométrographie and a method which related algebraic expressions to geometric objects. He has been called a co-founder of modern triangle geometry, as many of its characteristics are present in his work. (Full article...) -
Image 14
Amalie Emmy Noether (US: /ˈnʌtər/, UK: /ˈnɜːtə/; German: [ˈnøːtɐ]; 23 March 1882 – 14 April 1935) was a German mathematician who made many important contributions to abstract algebra. She proved Noether's first and second theorems, which are fundamental in mathematical physics. She was described by Pavel Alexandrov, Albert Einstein, Jean Dieudonné, Hermann Weyl and Norbert Wiener as the most important woman in the history of mathematics. As one of the leading mathematicians of her time, she developed theories of rings, fields, and algebras. In physics, Noether's theorem explains the connection between symmetry and conservation laws.
Noether was born to a Jewish family in the Franconian town of Erlangen; her father was the mathematician Max Noether. She originally planned to teach French and English after passing the required examinations but instead studied mathematics at the University of Erlangen, where her father lectured. After completing her doctorate in 1907 under the supervision of Paul Gordan, she worked at the Mathematical Institute of Erlangen without pay for seven years. At the time, women were largely excluded from academic positions. In 1915, she was invited by David Hilbert and Felix Klein to join the mathematics department at the University of Göttingen, a world-renowned center of mathematical research. The philosophical faculty objected, however, and she spent four years lecturing under Hilbert's name. Her habilitation was approved in 1919, allowing her to obtain the rank of Privatdozent. (Full article...) -
Image 15In classical mechanics, the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector (LRL vector) is a vector used chiefly to describe the shape and orientation of the orbit of one astronomical body around another, such as a binary star or a planet revolving around a star. For two bodies interacting by Newtonian gravity, the LRL vector is a constant of motion, meaning that it is the same no matter where it is calculated on the orbit; equivalently, the LRL vector is said to be conserved. More generally, the LRL vector is conserved in all problems in which two bodies interact by a central force that varies as the inverse square of the distance between them; such problems are called Kepler problems.
The hydrogen atom is a Kepler problem, since it comprises two charged particles interacting by Coulomb's law of electrostatics, another inverse-square central force. The LRL vector was essential in the first quantum mechanical derivation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom, before the development of the Schrödinger equation. However, this approach is rarely used today. (Full article...)
Good articles
-
Image 1

Farey sunburst of order 6, with 1 interior (red) and 96 boundary (green) points giving an area of 1 + 96/2 − 1 = 48
In geometry, Pick's theorem provides a formula for the area of a simple polygon with integer vertex coordinates, in terms of the number of integer points within it and on its boundary. The result was first described by Georg Alexander Pick in 1899. It was popularized in English by Hugo Steinhaus in the 1950 edition of his book Mathematical Snapshots. It has multiple proofs, and can be generalized to formulas for certain kinds of non-simple polygons. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Two random distributions on three-vertex binary trees, the binary search trees on three keys a, b, and c. These five trees are each assigned probability 1/5 by the uniform distribution (top). The distribution generated by random insertion orderings (bottom) assigns the center tree probability 1/3, because two of the six possible insertion orderings generate the same tree; the other four trees have probability 1/6.
In computer science and probability theory, a random binary tree is a binary tree selected at random from some probability distribution on binary trees. Different distributions have been used, leading to different properties for these trees.
Random binary trees have been used for analyzing the average-case complexity of data structures based on binary search trees. For this application it is common to use random trees formed by inserting nodes one at a time according to a random permutation. The resulting trees are very likely to have logarithmic depth and logarithmic Strahler number. The treap and related balanced binary search trees use update operations that maintain this random structure even when the update sequence is non-random. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Sir Isaac Newton (/ˈnjuːtən/; 25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, achieved the first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz. He contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science.
In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. He used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for tides, the trajectories of comets, the precession of the equinoxes and other phenomena, eradicating doubt about the Solar System's heliocentricity. Newton solved the two-body problem, and introduced the three-body problem. He demonstrated that the motion of objects on Earth and celestial bodies could be accounted for by the same principles. Newton's inference that the Earth is an oblate spheroid was later confirmed by the geodetic measurements of Maupertuis, La Condamine, and others, thereby convincing most European scientists of the superiority of Newtonian mechanics over earlier systems. (Full article...) -
Image 4

The logo of the International Mathematical Olympiad
The International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) is a mathematical olympiad for pre-university students, and is the oldest of the International Science Olympiads. It is widely regarded as the most prestigious mathematical competition in the world. The first IMO was held in Romania in 1959. It has since been held annually, except in 1980. More than 100 countries participate. Each country sends a team of up to six students, plus one team leader, one deputy leader, and observers.
Awards are given to approximately the top-scoring 50% of the individual contestants. Teams are not officially recognized—all scores are given only to individual contestants, but team scoring is unofficially compared more than individual scores. (Full article...) -
Image 5Basic Math is an educational video game for the Atari Video Computer System (Atari VCS). The game was developed at Atari, Inc. by Gary Palmer. The game involves a series of ten arithmetic problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. The player can edit different gameplay modes to alter how the numbers in the problem are chosen, or if their questions are timed. The game was released in 1977 as one of the earliest releases for the console.
The game is the only known game developed for the VCS by Palmer, who initially worked at Atari creating debugging stations for game developers, and later assisted with work on the Atari 400/800 line of computers. It was the first educational video game for the VCS, with others companies also releasing arithmetic-themed cartridges in the same year for the Fairchild Channel F and RCA Studio II. The game was also released under the title Fun with Numbers and Math. Both contemporary and retrospective reviews were generally unenthused by the game with common criticism being that it had poor quality graphics and was not appealing in terms of gameplay or control. (Full article...) -
Image 6

A spiral staircase in the Cathedral of St. John the Divine. Several helical curves in the staircase project to hyperbolic spirals in its photograph.
A hyperbolic spiral is a type of spiral with a pitch angle that increases with distance from its center, unlike the constant angles of logarithmic spirals or decreasing angles of Archimedean spirals. As this curve widens, it approaches an asymptotic line. It can be found in the view up a spiral staircase and the starting arrangement of certain footraces, and is used to model spiral galaxies and architectural volutes.
As a plane curve, a hyperbolic spiral can be described in polar coordinatesby the equation
for an arbitrary choice of the scale factor(Full article...)
-
Image 7
John von Neumann (/vɒn ˈnɔɪmən/ von NOY-mən; Hungarian: Neumann János Lajos [ˈnɒjmɒn ˈjaːnoʃ ˈlɒjoʃ]; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, integrating pure and applied sciences and making major contributions to many fields, including mathematics, physics, economics, computing, and statistics. He was a pioneer in building the mathematical framework of quantum physics, in the development of functional analysis, and in game theory, introducing or codifying concepts including cellular automata, the universal constructor and the digital computer. His analysis of the structure of self-replication preceded the discovery of the structure of DNA.
During World War II, von Neumann worked on the Manhattan Project. He developed the mathematical models behind the explosive lenses used in the implosion-type nuclear weapon. Before and after the war, he consulted for many organizations including the Office of Scientific Research and Development, the Army's Ballistic Research Laboratory, the Armed Forces Special Weapons Project and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. At the peak of his influence in the 1950s, he chaired a number of Defense Department committees including the Strategic Missile Evaluation Committee and the ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee. He was also a member of the influential Atomic Energy Commission in charge of all atomic energy development in the country. He played a key role alongside Bernard Schriever and Trevor Gardner in the design and development of the United States' first ICBM programs. At that time he was considered the nation's foremost expert on nuclear weaponry and the leading defense scientist at the U.S. Department of Defense. (Full article...) -
Image 8

In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and the hypotenuse c, sometimes called the Pythagorean equation:
:
The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proved numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. (Full article...) -
Image 9
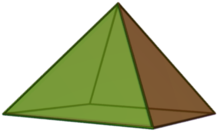
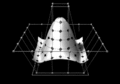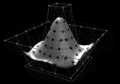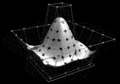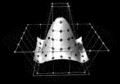
In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid with a square base, having a total of five faces. If the apex of the pyramid is directly above the center of the square, it is a right square pyramid with four isosceles triangles; otherwise, it is an oblique square pyramid. When all of the pyramid's edges are equal in length, its triangles are all equilateral. It is called an equilateral square pyramid, an example of a Johnson solid.
Square pyramids have appeared throughout the history of architecture, with examples being Egyptian pyramids and many other similar buildings. They also occur in chemistry in square pyramidal molecular structures. Square pyramids are often used in the construction of other polyhedra. Many mathematicians in ancient times discovered the formula for the volume of a square pyramid with different approaches. (Full article...) -
Image 10

A unit distance graph with 16 vertices and 40 edges
In mathematics, particularly geometric graph theory, a unit distance graph is a graph formed from a collection of points in the Euclidean plane by connecting two points whenever the distance between them is exactly one. To distinguish these graphs from a broader definition that allows some non-adjacent pairs of vertices to be at distance one, they may also be called strict unit distance graphs or faithful unit distance graphs. As a hereditary family of graphs, they can be characterized by forbidden induced subgraphs. The unit distance graphs include the cactus graphs, the matchstick graphs and penny graphs, and the hypercube graphs. The generalized Petersen graphs are non-strict unit distance graphs.
An unsolved problem of Paul Erdős asks how many edges a unit distance graph onvertices can have. The best known lower bound is slightly above linear in
—far from the upper bound, proportional to
. The number of colors required to color unit distance graphs is also unknown (the Hadwiger–Nelson problem): some unit distance graphs require five colors, and every unit distance graph can be colored with seven colors. For every algebraic number there is a unit distance graph with two vertices that must be that distance apart. According to the Beckman–Quarles theorem, the only plane transformations that preserve all unit distance graphs are the isometries. (Full article...)
-
Image 11
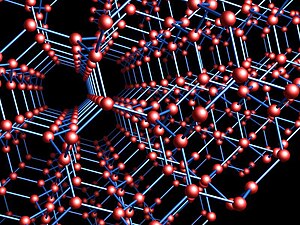
The Laves graph
In geometry and crystallography, the Laves graph is an infinite and highly symmetric system of points and line segments in three-dimensional Euclidean space, forming a periodic graph. Three equal-length segments meet at 120° angles at each point, and all cycles use ten or more segments. It is the shortest possible triply periodic graph, relative to the volume of its fundamental domain. One arrangement of the Laves graph uses one out of every eight of the points in the integer lattice as its points, and connects all pairs of these points that are nearest neighbors, at distance. It can also be defined, divorced from its geometry, as an abstract undirected graph, a covering graph of the complete graph on four vertices.
H. S. M. Coxeter (1955) named this graph after Fritz Laves, who first wrote about it as a crystal structure in 1932. It has also been called the K4 crystal, (10,3)-a network, diamond twin, triamond, and the srs net. The regions of space nearest each vertex of the graph are congruent 17-sided polyhedra that tile space. Its edges lie on diagonals of the regular skew polyhedron, a surface with six squares meeting at each integer point of space. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Mathematics in art: Albrecht Dürer's copper plate engraving Melencolia I, 1514. Mathematical references include a compass for geometry, a magic square and a truncated rhombohedron, while measurement is indicated by the scales and hourglass.
Mathematics and art are related in a variety of ways. Mathematics has itself been described as an art motivated by beauty. Mathematics can be discerned in arts such as music, dance, painting, architecture, sculpture, and textiles. This article focuses, however, on mathematics in the visual arts.
Mathematics and art have a long historical relationship. Artists have used mathematics since the 4th century BC when the Greek sculptor Polykleitos wrote his Canon, prescribing proportions conjectured to have been based on the ratio 1:√2 for the ideal male nude. Persistent popular claims have been made for the use of the golden ratio in ancient art and architecture, without reliable evidence. In the Italian Renaissance, Luca Pacioli wrote the influential treatise De divina proportione (1509), illustrated with woodcuts by Leonardo da Vinci, on the use of the golden ratio in art. Another Italian painter, Piero della Francesca, developed Euclid's ideas on perspective in treatises such as De Prospectiva Pingendi, and in his paintings. The engraver Albrecht Dürer made many references to mathematics in his work Melencolia I. In modern times, the graphic artist M. C. Escher made intensive use of tessellation and hyperbolic geometry, with the help of the mathematician H. S. M. Coxeter, while the De Stijl movement led by Theo van Doesburg and Piet Mondrian explicitly embraced geometrical forms. Mathematics has inspired textile arts such as quilting, knitting, cross-stitch, crochet, embroidery, weaving, Turkish and other carpet-making, as well as kilim. In Islamic art, symmetries are evident in forms as varied as Persian girih and Moroccan zellige tilework, Mughal jali pierced stone screens, and widespread muqarnas vaulting. (Full article...)
Did you know
- ... that Catechumen, a Christian first-person shooter, was funded only in the aftermath of the Columbine High School massacre?
- ... that Ukrainian baritone Danylo Matviienko, who holds a master's degree in mathematics, appeared as Demetrius in Britten's opera A Midsummer Night's Dream at the Oper Frankfurt?
- ... that Fairleigh Dickinson's upset victory over Purdue was the biggest upset in terms of point spread in NCAA tournament history, with Purdue being a 23+1⁄2-point favorite?
- ... that in 1940 Xu Ruiyun became the first Chinese woman to receive a PhD in mathematics?
- ... that Ewa Ligocka cooked another mathematician's goose?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that despite published scholarship to the contrary, Andrew Planta neither received a doctorate nor taught mathematics at Erlangen?
- ... that circle packings in the form of a Doyle spiral were used to model plant growth long before their mathematical investigation by Doyle?

- ...that people are significantly slower to identify the parity of zero than other whole numbers, regardless of age, language spoken, or whether the symbol or word for zero is used?
- ...that Auction theory was successfully used in 1994 to sell FCC airwave spectrum, in a financial application of game theory?
- ...properties of Pascal's triangle have application in many fields of mathematics including combinatorics, algebra, calculus and geometry?
- ...work in artificial intelligence makes use of swarm intelligence, which has foundations in the behavioral examples found in nature of ants, birds, bees, and fish among others?
- ...that statistical properties dictated by Benford's Law are used in auditing of financial accounts as one means of detecting fraud?
- ...that modular arithmetic has application in at least ten different fields of study, including the arts, computer science, and chemistry in addition to mathematics?
- ... that according to Kawasaki's theorem, an origami crease pattern with one vertex may be folded flat if and only if the sum of every other angle between consecutive creases is 180º?
Showing 7 items out of 75
Featured pictures
-
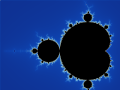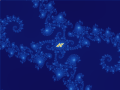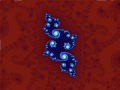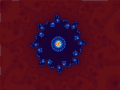
Image 2Mandelbrot set, step 1, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 3Proof of the Pythagorean theorem, by Joaquim Alves Gaspar (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 4Mandelbrot set, step 10, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 6Mandelbrot set, step 11, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 7Mandelbrot set, step 2, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 8Mandelbrot set, step 4, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 9Mandelbrot set, step 3, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 10Line integral of scalar field, by Lucas V. Barbosa (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 11Mandelbrot set, step 9, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 12Mandelbrot set, step 8, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 13Tetrahedral group at Symmetry group, by Debivort (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 14Mandelbrot set, step 12, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 16Mandelbrot set, start, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 17Fields Medal, front, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
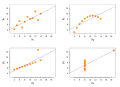
Image 18Anscombe's quartet, by Schutz (edited by Avenue) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 19Mandelbrot set, step 14, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 20Mandelbrot set, step 13, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 22Hypotrochoid, by Sam Derbyshire (edited by Anevrisme and Perhelion) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 23Mandelbrot set, step 6, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 24Mandelbrot set, by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 25Desargues' theorem, by Dynablast (edited by Jujutacular and Julia W) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 28Lorenz attractor at Chaos theory, by Wikimol (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 29Mandelbrot set, step 5, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 32Mandelbrot set, step 7, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 33Cellular automata at Reflector (cellular automaton), by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 34Fields Medal, back, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
Get involved
- For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Mathematics-related articles, visit WikiProject Mathematics.
Categories
Topics
Index of articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Vital articles
- » subpages: Level 4 Mathematics articles, Level 5 Mathematics articles
Discover Wikipedia using portals
Previous Page Next Page



![Image 1 Portrait by August Köhler, c. 1910, after 1627 original Johannes Kepler (/ˈkɛplər/; German: [joˈhanəs ˈkɛplɐ, -nɛs -] ⓘ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonice Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae, influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel Somnium. Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, being named the father of modern optics, in particular for his Astronomiae pars optica. He also invented an improved version of the refracting telescope, the Keplerian telescope, which became the foundation of the modern refracting telescope, while also improving on the telescope design by Galileo Galilei, who mentioned Kepler's discoveries in his work. He is also known for postulating the Kepler conjecture. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)