Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Hexabenzocoronene
| |||
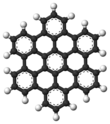
 AFM image of hexabenzocoronene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexabenzo[bc,ef,hi,kl,no,qr]coronene | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C42H18 | |||
| Molar mass | 522.606 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | dark yellow[1] | ||
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 (calc.)[1] | ||
| -346.0·10−6 cm3/mol[2] | |||
| Structure[1] | |||
| monoclinic, P21/a | |||
a = 1.8431(3) nm, b = 0.5119(1) nm, c = 1.2929(2) nm α = 90°, β = 112.57(1)°, γ = 90°
| |||
Formula units (Z)
|
2 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
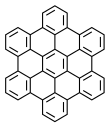
Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C42H18. It consists of a central coronene molecule, with an additional benzene ring fused between each adjacent pair of rings around the periphery. It is sometimes simply called hexabenzocoronene, however, there are other chemicals that share this less-specific name, such as hexa-cata-hexabenzocoronene.
Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene has been imaged by atomic force microscopy (AFM) providing the first example of a molecule in which differences in bond order and bond lengths of the individual bonds can be distinguished by a measurement in direct space.[3]
- ^ a b c Goddard, Richard; Haenel, Matthias W.; Herndon, William C.; Krueger, Carl; Zander, Maximilian (1995). "Crystallization of Large Planar Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: The Molecular and Crystal Structures of Hexabenzo[bc,ef,hi,kl,no,qr]coronene and Benzo[1,2,3-bc:4,5,6-b'c']dicoronene". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 117: 30–41. doi:10.1021/ja00106a004.
- ^ Akamatu, Hideo; Kinoshita, Minoru (1959). "On the Magnetic Susceptibility of Hexabenzocoronene and Triphenylene". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 32 (7): 773–774. doi:10.1246/bcsj.32.773.
- ^ Gross, L.; Mohn, F.; Moll, N.; Schuler, B.; Criado, A.; Guitian, E.; Pena, D.; Gourdon, A.; Meyer, G. (2012). "Bond-Order Discrimination by Atomic Force Microscopy". Science. 337 (6100): 1326–9. Bibcode:2012Sci...337.1326G. doi:10.1126/science.1225621. PMID 22984067. S2CID 206542919.
Previous Page Next Page