Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Monohydrogen phosphate
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hydrogenphosphate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Monohydrogenphosphate Phosphoric acid, ion(2-) | |||
| Other names
Phosphoric acid, ion(2-)
Hydrophosphoric acid (2-) Biphosphate (2-) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| 1998 | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
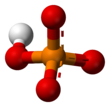
| HPO2− 4 | |||
| Conjugate acid | Dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| Conjugate base | Phosphate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Hydrogen phosphate or monohydrogen phosphate (systematic name) is the inorganic ion with the formula [HPO4]2-. Its formula can also be written as [PO3(OH)]2-. Together with dihydrogen phosphate, hydrogenphosphate occurs widely in natural systems. Their salts are used in fertilizers and in cooking.[1] Most hydrogenphosphate salts are colorless, water soluble, and nontoxic.
It is a conjugate acid of phosphate [PO4]3- and a conjugate base of dihydrogen phosphate [H2PO4]−.
It is formed when a pyrophosphate anion [P
2O
7]4−
reacts with water H
2O by hydrolysis, which can give hydrogenphosphate:
- [P
2O
7]4−
+ H2O ⇌ 2 [HPO
4]2−
- ^ Schrödter, Klaus; Bettermann, Gerhard; Staffel, Thomas; Wahl, Friedrich; Klein, Thomas; Hofmann, Thomas (2008). "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
Previous Page Next Page