Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Pancreatitis
| Pancreatitis | |
|---|---|
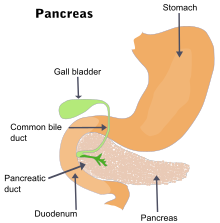 | |
| The pancreas and surrounding organs | |
| Specialty | |
| Symptoms | |
| Complications | Infection, bleeding, diabetes mellitus,[1] pancreatic cancer, kidney failure, breathing problems, malnutrition[2] |
| Duration | Short or long term[1] |
| Causes | |
| Risk factors | Smoking[3][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, blood amylase or lipase[5][1] |
| Treatment | Intravenous fluids, pain medication, antibiotics[1] |
| Frequency | 8.9 million (2015)[6] |
| Deaths | 132,700 (2015)[7] |
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas.[1] The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones.[1] There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis.[1] Signs and symptoms of pancreatitis include pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting.[1] The pain often goes into the back and is usually severe.[1] In acute pancreatitis, a fever may occur; symptoms typically resolve in a few days.[1] In chronic pancreatitis, weight loss, fatty stool, and diarrhea may occur.[1][5] Complications may include infection, bleeding, diabetes mellitus, or problems with other organs.[1]
The two most common causes of acute pancreatitis are a gallstone blocking the common bile duct after the pancreatic duct has joined; and heavy alcohol use.[1] Other causes include direct trauma, certain medications, infections such as mumps, and tumors.[1] Chronic pancreatitis may develop as a result of acute pancreatitis.[1] It is most commonly due to many years of heavy alcohol use.[1] Other causes include high levels of blood fats, high blood calcium, some medications, and certain genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, among others.[1] Smoking increases the risk of both acute and chronic pancreatitis.[3][4] Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is based on a threefold increase in the blood of either amylase or lipase.[1] In chronic pancreatitis, these tests may be normal.[1] Medical imaging such as ultrasound and CT scan may also be useful.[1]
Acute pancreatitis is usually treated with intravenous fluids, pain medication, and sometimes antibiotics.[1] For patients with severe pancreatitis who cannot tolerate normal oral food consumption, a nasogastric tube is placed in the stomach.[1][8] A procedure known as an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be done to examine the distal common bile duct and remove a gallstone if present.[1] In those with gallstones the gallbladder is often also removed.[1] In chronic pancreatitis, in addition to the above, temporary feeding through a nasogastric tube may be used to provide adequate nutrition.[1] Long-term dietary changes and pancreatic enzyme replacement may be required.[1] Occasionally, surgery is done to remove parts of the pancreas.[1]
Globally, in 2015 about 8.9 million cases of pancreatitis occurred.[6] This resulted in 132,700 deaths, up from 83,000 deaths in 1990.[7][9] Acute pancreatitis occurs in about 30 per 100,000 people a year.[3] New cases of chronic pancreatitis develop in about 8 per 100,000 people a year and currently affect about 50 per 100,000 people in the United States.[10] It is more common in men than women.[1] Often chronic pancreatitis starts between the ages of 30 and 40 and is rare in children.[1] Acute pancreatitis was first described on autopsy in 1882 while chronic pancreatitis was first described in 1946.[10]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae "Pancreatitis". The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. National Institutes of Health. August 16, 2012. Archived from the original on 7 March 2015. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Patient Care & Health Information > Diseases & Conditions: Pancreatitis". Mayo Clinic. 4 June 2022.
- ^ a b c Lankisch PG, Apte M, Banks PA (July 2015). "Acute pancreatitis". Lancet. 386 (9988): 85–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60649-8. hdl:1959.4/unsworks_49570. PMID 25616312. S2CID 25600369.
- ^ a b Yadav D, Lowenfels AB (June 2013). "The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer". Gastroenterology. 144 (6): 1252–1261. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.068. PMC 3662544. PMID 23622135.
- ^ a b Witt H, Apte MV, Keim V, Wilson JS (April 2007). "Chronic pancreatitis: challenges and advances in pathogenesis, genetics, diagnosis, and therapy". Gastroenterology. 132 (4): 1557–1573. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.001. PMID 17466744.
- ^ a b Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ a b Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al. (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ Tenner S, Vege SS, Sheth SG, Sauer B, Yang A, Conwell DL, et al. (March 2024). "American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: Management of Acute Pancreatitis". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 119 (3): 419–437. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000002645. PMID 38857482.
- ^ GBD 2013 Mortality Causes of Death Collaborators (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- ^ a b Muniraj T, Aslanian HR, Farrell J, Jamidar PA (December 2014). "Chronic pancreatitis, a comprehensive review and update. Part I: epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, genetics, pathophysiology, and clinical features". Disease-a-Month. 60 (12): 530–550. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2014.11.002. PMID 25510320.
Previous Page Next Page


