Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Viruses
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
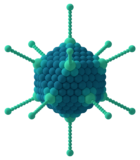
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease

Meningitis is an acute inflammation of the meninges, protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms in adults include headache, fever and neck stiffness, as well as sometimes confusion or altered consciousness, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Children often show only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability or drowsiness.
The most common cause is infection with viruses including enteroviruses, herpes simplex virus (mainly HSV-2), varicella zoster virus, mumps virus, HIV and lymphocytic choriomeningitis. In Western countries, viral meningitis occurs in around 11 people per 100,000 each year. Infection with bacteria, fungi, protozoa and parasites can also cause meningitis, and there are several non-infectious causes. Although some forms of meningitis can be life-threatening, viral meningitis is generally more benign than that caused by bacterial infection. It usually resolves spontaneously and is rarely fatal. HSV-2 can cause a chronic, recurrent form called Mollaret's meningitis.
Polymerase chain reaction of cerebrospinal fluid and identification of antibodies can be used to differentiate between viral causes. Viral meningitis typically only requires supportive therapy; meningitis caused by HSV or varicella zoster virus sometimes responds to treatment with antiviral drugs such as aciclovir. Mumps-associated meningitis can be prevented by vaccination.
Selected image
The striping caused by tulip breaking virus, first described in 1576 by Carolus Clusius, was the second plant virus disease to be documented. The effects were much prized by 17th-century tulip growers.
Credit: Unknown (before 1640)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Viruses and viral infections have affected human history. Epidemics caused by viruses began when human behaviour changed during the Neolithic period, around 12,000 years ago. Previously hunter-gatherers, humans developed more densely populated agricultural communities, which allowed viruses to spread rapidly and subsequently to become endemic. Viruses of plants and livestock also increased, and as humans became dependent on agriculture and farming, diseases such as potyviruses of potatoes and rinderpest of cattle had devastating consequences. Smallpox and measles viruses are among the oldest that infect humans. They first appeared in humans in Europe and North Africa thousands of years ago, having evolved from viruses that infected other animals. Influenza pandemics have been recorded since 1580.
There are an estimated 1031 viruses on Earth. Although scientific interest in them arose because of the diseases they cause, most viruses are beneficial. They drive evolution by transferring genes across species, play important roles in ecosystems, and are essential to life.
Selected outbreak
The West African Ebola epidemic was the most widespread outbreak of the disease to date. Beginning in Meliandou in southern Guinea in December 2013, it spread to adjacent Liberia and Sierra Leone, affecting the cities of Conakry and Monrovia, with minor outbreaks in Mali and Nigeria. Cases reached a peak in October 2014 and the epidemic was under control by late 2015, although occasional cases continued to occur into April 2016. Ring vaccination with the then-experimental vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV was trialled in Guinea.
More than 28,000 suspected cases were reported with more than 11,000 deaths; the case fatality rate was around 40% overall and around 58% in hospitalised patients. Early in the epidemic nearly 10% of the dead were healthcare workers. The outbreak left about 17,000 survivors, many of whom reported long-lasting post-recovery symptoms. Extreme poverty, dysfunctional healthcare systems, distrust of government after years of armed conflict, local burial customs of washing the body, the unprecedented spread of Ebola to densely populated cities, and the delay in response of several months all contributed to the failure to control the epidemic.
Selected quotation
| “ | The unusual features of the giant Mimivirus revived the popular, yet unresolved question: "Are viruses alive?" The discovery that some of them can get sick adds a new twist to this old debate. | ” |
—Hiroyuki Ogata & Jean-Michel Claverie on the relationship between Sputnik virophage and mimivirus
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Adenoviruses are a group of non-enveloped DNA viruses that make up the Adenoviridae family. At 90–100 nm in diameter, they are the largest known viruses to lack an envelope. Unique spikes or fibres protrude from the icosahedral capsid, with knobs that bind to the receptor on the host cell. The linear double-stranded genome is 26 to 48 kb long, encodes 23 to 46 proteins, and has a 55 kDa protein attached to each end.
Adenoviruses infect a broad range of vertebrates, including humans, livestock, horses, dogs, bats and other mammals, as well as birds and reptiles, and usually cause infections of the upper respiratory tract. The virus is very stable. Transmission can occur by respiratory droplets or via faeces, with swimming pools being a common source of infection. A total of 57 serotypes, grouped into 7 species, have been found in humans; they cause a wide range of illnesses including mild respiratory infections, conjunctivitis and gastroenteritis. Some types have been associated with obesity. In people with an immunodeficiency they can cause life-threatening multi-organ disease. No antiviral treatment or vaccine is generally available; hand washing is the best way to prevent infection. Adenoviruses are an important viral vector for gene therapy. An oncolytic adenovirus has been approved in China for the treatment of head and neck cancer.
Did you know?
- ...that the stripes on tulips (examples pictured) that caused tulip mania were probably caused by a virus, but this was unknown to science at the time?
- ...that epidemiologist Li Lanjuan was the first to propose a lockdown of Wuhan during the 2019–20 coronavirus outbreak?
- ...that the human bocavirus is the fourth most commonly found virus in samples collected from the respiratory system?
- ...that research by Harold Ginsberg on adenoviruses led to the development of gene therapy, in which modified versions of viruses can be used to implant healthy versions of genes to treat disease?
- ...that the Tiverton fire of 1731 resulted in an increased incidence of smallpox?
Selected biography
Peter Piot (born 17 February 1949) is a Belgian virologist and public health specialist, known for his work on Ebola virus and HIV.
During the first outbreak of Ebola in Yambuku, Zaire in 1976, Piot was one of a team that discovered the filovirus in a blood sample. He and his colleagues travelled to Zaire to help to control the outbreak, and showed that the virus is transmitted via blood and during preparation of bodies for burial. He advised WHO during the West African Ebola epidemic of 2014–16.
In the 1980s, Piot participated in collaborative projects in Burundi, Côte d'Ivoire, Kenya, Tanzania and Zaire, including Project SIDA in Kinshasa, the first international project on AIDS in Africa, which provided the foundations for understanding HIV infection in that continent. He was the founding director of UNAIDS, and has served as president of the International AIDS Society and assistant director of the WHO Global HIV/AIDS Programme. As of 2020, he directs the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
In this month
1 January 1934: Discovery of mumps virus by Claud Johnson and Ernest Goodpasture
1 January 1942: Publication of George Hirst's paper on the haemagglutination assay
1 January 1967: Start of WHO intensified eradication campaign for smallpox (vaccination kit pictured)
3 January 1938: Foundation of March of Dimes, to raise money for polio
6 January 2011: Andrew Wakefield's paper linking the MMR vaccine with autism described as "fraudulent" by the BMJ
25 January 1988: Foundation of the International AIDS Society
29 January 1981: Influenza haemagglutinin structure published by Ian Wilson, John Skehel and Don Wiley, the first viral membrane protein whose structure was solved
Selected intervention
Zidovudine (ZDV) (also known as AZT and sold as Retrovir) is an antiretroviral drug used in the prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS. Classed as a nucleoside analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitor, it inhibits HIV's reverse transcriptase enzyme, which copies the viral RNA into DNA and is essential for its replication. The first breakthrough in AIDS therapy, ZDV was licensed in 1987. While it significantly reduces HIV replication, leading to some clinical and immunological benefits, when used alone ZDV does not completely stop replication, allowing the virus to become resistant to it. The drug is therefore used together with other anti-HIV drugs in combination therapy called highly active antiretroviral therapy. To simplify its administration, ZDV is included in combination pills with lamivudine (Combivir) and lamivudine plus abacavir (Trizivir). ZDV continues to be used to prevent HIV transmission from mother to child during childbirth; it was previously part of the standard post-exposure prophylaxis after needlestick injury.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Previous Page Next Page