Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Caribbean
| Main Portal page | Indices | Projects |
 |
 |

| |
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ib-EE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/ KARR-ib-ee-an; Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben) is a subregion in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo islands and Belizean islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, and Corn Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the continental mainland of the Americas bordering the region from the Yucatán Peninsula in North America through Central America to the Guianas in South America. (Full article...)
Zombia antillarum, commonly known as the zombie palm, is a species of palm tree and the only member of the genus Zombia. It is endemic to the island of Hispaniola (both the Dominican Republic and Haiti) in the Greater Antilles. Usually found in dry, hilly areas of northern and southern Haiti and the northwest of the Dominican Republic, Z. antillarum is a relatively short fan palm with clustered stems and a very distinctive appearance caused by its persistent spiny leaf sheaths. Threatened by habitat destruction in Haiti, Z. antillarum is a popular ornamental species due to its distinctive appearance, low maintenance requirements and salt tolerance. (Full article...)
Selected geography article -
Saint Thomas (Danish: Sankt Thomas, Spanish: Santo Tomás, French: Saint-Thomas) is one of the Virgin Islands in the Caribbean Sea, and a constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States. Along with surrounding minor islands, it is one of three county equivalents in the USVI. Together with Saint John, it forms one of the districts of the USVI. The territorial capital and port of Charlotte Amalie is located on the island.
Of the three islands, St. Thomas is the second largest, with St. Croix being the largest, and St. John, the smallest. As of the 2010 census, the population of Saint Thomas was 51,634, about 48.5% of the total population of the United States Virgin Islands. Crown Mountain is the highest point in Saint Thomas and in the entire United States Virgin Islands. Hence, it is called "Rock City". The island has a land area of 32 square miles (83 km2). (Full article...)
Selected fare or cuisine -
Goat water, also referred to as kiddy stew, is a stew that is a part of the national cuisine of the Caribbean island of Montserrat. It has been described as a national dish of Montserrat. It has also been described as a national stew.
Goat water is prepared using goat meat, onions, herbs and chible (scallions/spring onions and thyme), hot green pepper, salt and pepper to taste, garlic, cloves, oil, water, marjoram, ground mace, and flour. It is sometimes served with rice or crispy bread rolls. The dish has been described as spicy and flavorful. (Full article...)
Did you know? -
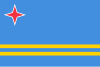
- ...that on 16 February 1942, an oil processing refinery in the Lesser Antilles island of Aruba (flag pictured) was attacked by a German submarine?
- ...that Cubavision International broadcasts throughout the world?
- ...that Stern John is Trinidad and Tobago's leading goalscorer in international football, and scored 68 goals in 100 games?
Related portals
Wikiproject
The golden swallow (Tachycineta euchrysea) is a swallow endemic to the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and was once native to Jamaica, but is now extirpated there. It is restricted to isolated montane forests that primarily consist of the Hispaniolan pine (Pinus occidentalis). This species is considered to be a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The exact cause of its extirpation from Jamaica is unknown, but likely factors include predation by introduced mammals and habitat loss, although the habitat loss theory is not supported by much evidence. The last sighting of the nominate subspecies was in Hardwar Gap (located on the boundary between Saint Andrew and Portland parishes), with three birds being seen on 8 June 1989.
A relatively small swallow, the Jamaican subspecies had bronze upperparts and bronze sides of the head. The ears and lores were duller and the forehead area was more green than bronze. The shoulders, back, rump, and uppertail-coverts were, on the other hand, a coppery-bronze colour. The lesser and median coverts were more coppery, with the greater and primary-wing-coverts more of a dusky green. The primaries, secondaries, and tail were a dusky bronze-green. The underparts were mostly white. The legs, feet, and irides were dark brown, and the bill was black. The female was similar, but with its breast, and occasionally throat and undertail-coverts, mottled grey-brown. The juvenile was also mottled-grey brown, and duller overall. The Hispaniolan subspecies, T. e. sclateri, is primarily differentiated by its more deeply forked tail, blue-green forehead and uppertail-coverts, and blue-black wings and tail. (Full article...)
Selected image -

Photograph of Jamaican political activist Marcus Garvey in 1924.
Selected music -
The music of Guadeloupe encompasses a large popular music industry, which gained in international renown after the success of zouk music in the later 20th century. Zouk's popularity was particularly intense in France, where the genre became an important symbol of identity for Guadeloupe and Martinique. Zouk's origins are in the folk music of Guadeloupe and Martinique, especially Guadeloupan gwo ka and Martinican chouval bwa, and the pan-Caribbean calypso tradition. (Full article...)
General images
Caribbean topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2025-02-02 19:56 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Leroy King (Antigua and Barbuda) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mediascriptor (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 32
- 19th Africa Movie Academy Awards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 16
- Kyle Ming (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (196)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 24
- Kemar Foster (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (196)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 16
- Danté Cassanova (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (196)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 24
- Stephen McClashie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2025-02-02, score: 16
- Lawrence Maxwell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (167)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- List of phyllostomids (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PresN (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 80
- Barbudan Creole (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 48
- South Antiguan Creole (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 32
- North Antiguan Creole (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 67
- Dulichiella appendiculata (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JGBlue1509 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- Languages of Antigua and Barbuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 64
- Tyto cravesae (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anteosaurus magnificus (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- Tulio O'Neill O'Keefe (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Technopat (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 36
- Mario de Miranda (bridge engineer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fedem (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 28
- List of Seattle Sounders FC draft picks (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SounderBruce (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- 1894 Florida Panhandle hurricane (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 12george1 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 40
- The Hague Group (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ras al Ghoul (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- Conchoprimo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Altenmann (talk · contribs · new pages (260)) started on 2025-02-01, score: 16
- Deaths in October 1985 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Drewsky1211 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Elsie Calderón (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ivan Quiles (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Durity (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Qaswa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Guerline Jozef (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rubystaramaryllis (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Yaxel Lendeborg (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BeanieFan11 (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 24
- Virgin Islands men's national under-17 and under-18 basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Maiō T. (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Ebony Cham (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CassiJevenn (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Intelligence Centre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 32
- A. aeneus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jlwoodwa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Michael Palmer (cricketer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pkr206 (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 24
- The Leap (film) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rickyurs (talk · contribs · new pages (63)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Dominican Republic at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Dominica at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Anba dlo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rickyurs (talk · contribs · new pages (63)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 32
- Alberto de Quintana y Combis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Hiros (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MrMaster17 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- List of PDK International chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- A. papillata (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jlwoodwa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- A. nuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jlwoodwa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-31, score: 16
- Spanish frigate Navas de Tolosa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mdnavman (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 24
- Fayolle Jean (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (121)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Leiocephalus anonymous (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Marcos Rodríguez Bobadilla (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 32
- Fayolle Jean Jr. (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (121)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Leiocephalus apertosulcus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Marcos Rodríguez Bobadilla (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 32
- US Virgin Islands Division of Fish and Wildlife (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Auratus Nicole (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Maria Elena Cruz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ErieSwiftByrd (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- 2025 Anguillian general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sundostund (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Curaçao at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- A. conferta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jlwoodwa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Widemir Normil (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (121)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Lillie Maie Hubbard (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Penny Richards (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Cuba at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- A. ciliata (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jlwoodwa (talk · contribs · new pages (99)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Cornelius Tulloch (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Raneemh (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Marianly Tejada (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (196)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- English ship Gillyflower (1651) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lyndaship (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-01-30, score: 16
- Eoo (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gelo DemonPlayer (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 16
- United Progressive Party (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 48
- National Liberation Front of Corsica (1976-1990) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Charlottevittori (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 48
- Terrence Deyalsingh (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 24
- Catalina de Medrano (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by The Royal Herald (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 24
- José Llovera (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 16
- Christina Leslie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Medievalfran (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 32
- Clover Graham (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Medievalfran (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 16
- Kaylee Hunter (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedPatch (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 16
- Timeline of the Gaza war (12 January 2024 – 6 May 2024) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Amakuru (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 24
- List of storms named Elvis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sleepinthestars (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-29, score: 16
- USCGC Farallon (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jordanroderick (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 64
- 2025 Baseball Champions League Americas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GreenRunner0 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 24
- 2024–25 UNC Wilmington Seahawks women's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedSox39 (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 16
- Louis de Souza (barrister) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ashlar (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 40
- Saint-Barthélemy affair (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dencoolast33 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 40
- 2023 FIBA U17 Centrobasket (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Maiō T. (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 16
- 2025 IHF Inter-Continental Trophy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Almagestas (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 16
- Robert Bowcher Clarke (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ashlar (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 40
- IQ Option (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kahvihenki (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 24
- Floyd Mayweather Jr. vs. Henry Bruseles (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beast from da East (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 16
- Sanderford Jarman (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LydiaRaeW (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-28, score: 16
- Rainier Mallol (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Conlosardientes55 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Jesús Santa Aponte (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ivan Quiles (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Beekeeping in Antigua and Barbuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 64
- Francisco Arce (disambiguation) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ortizesp (talk · contribs · new pages (81)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Cayman Islands at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Copyright law of Aruba (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Martsniez (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Rob Harley (American football) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cbowers77 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Widline Cadet (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bookworm-ce (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Puerto Rico men's national under-19 basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Maiō T. (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Stan Oduma Smith (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 24eeWikiUser (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 40
- Jamby (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HourglassTears (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Michael Joseph (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 32
- Rodney Williams (disambiguation) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 32
- Telbert Benjamin (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 32
- Muerte en Hawáii (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Carlosmarkos2345 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-27, score: 16
- Robert Garland Colodny (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Asparagirl (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- List of executive air transports of U.S. states (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gimelthedog (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- FIBA U17 Centrobasket (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Maiō T. (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 35
- 2025 Serie de las Américas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RossGA 19 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 32
- List of awards and nominations received by Natti Natasha (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Monika Helgesson (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 24
- Agriculture in Antigua and Barbuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 40
- Jamby El Favo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PlainWatcher (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 24
- Her Royal Majesty Queen-mother Sêmévo 1st (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Iambl (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- Bahamas at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- Aruba at the 2024 World Aquatics Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WildCherry06 (talk · contribs · new pages (74)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- Epic Colocotronis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jno.skinner (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 16
- Jean-Victor Harvel Jean-Baptiste (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robinsonodora (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 24
- Ahmed Saba (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Frank Ken (talk · contribs · new pages (109)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 16
- List of fatal dog attacks in France (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wikigrund (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- Jorge Pierluisi Diaz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 24
- Documented (news organization) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MSG17 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 16
- Alexandra Davis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Assefaa (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 32
- Kashif Ali (cricketer, born 1994) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 16
- Business ventures and estate owned by Miguel Enríquez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Caribbean H.Q. (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 72
- The Best of Menudo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Markus WikiEditor (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 16
- Furcaspis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Edibobb (talk · contribs · new pages (76)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- Nancy Ostrander (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Topsyturvy2 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- Forts of Enxara (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roundtheworld (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 24
- Antonio Peláez de Campomanes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 24
- Francisco Campos (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shhhnotsoloud (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- Antigua Broadcasting Service (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 40
- Tyson Dupont (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rickyc123 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- Vivre Libre ou Mourir (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kevin9217 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 16
- List of African film festivals (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ceslause (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 32
- Surrender of Saint Barthélemy (1801) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gvssy (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 24
- In Action (Menudo album) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Markus WikiEditor (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 16
- 1963 in Costa Rica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spideog (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 27
- Sebastián Acuña (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cazza3012 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 27
- SVG-TV (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 32
- BKEX (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Salvationist2nd (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 16
- Gregorio Hontomin (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JB Hoang Tam 2 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 16
- Donald Trump and religion (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nikkimaria (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 16
- Corruption in Suriname (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DaltonCastle (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 80
- TV Around the World (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bkissin (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 40
- Second Anglo–Ashanti War (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Setergh (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 16
- Women's Golf Day (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WGD Willem (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2025-01-10, score: 16
- Southern Command Network (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 24
- Manchester United Calypso (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ersene (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 16
- Leiocephalus altavelensis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Marcos Rodríguez Bobadilla (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- Law on Departmentalization (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JASpencer (talk · contribs · new pages (164)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 64
- List of executive orders in the second presidency of Donald Trump (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AndrewRT (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- First 100 days of the second Donald Trump presidency (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (40)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- 10th Grenadian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 473Camerhogne (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- 11th Grenadian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 473Camerhogne (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- 1967 Men's World Tennis Circuit (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Navops47 (talk · contribs · new pages (85)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 24
- Kalilou Singhateh (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jmanlucas (talk · contribs · new pages (45)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- Johnny Rivera (wrestler) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kingzwest (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- Vial Autopista–Artemisa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CubanoBoi (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 16
- Tremella compacta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RunningClam (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 40
- Gina Brillon (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Comedyenthusiast (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- List of Delta Theta Phi chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Grand Fond, Dominica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 32
- Executive Government Council (Haiti) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBrowniess (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 16
- Bagatelle, Dominica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (59)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Choranthus orientis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeffreyGammon (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 32
- Ash Holme (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Meena (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Acrosternum marginatum (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeffreyGammon (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 32
- Choranthus antiqua (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeffreyGammon (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 56
- Antigua Barbuda Global Music & Media Awards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mediascriptor (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 51
- Raiz No Rama World Tour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DivaKnockouts (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Diamante (wrestler, born 1991) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 162 etc. (talk · contribs · new pages (49)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- List of Alpha Phi Sigma chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Allobates caribe (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Darkfrog24 (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 16
- Skylarking (Horace Andy song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Humbledaisy (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
- Modern great power (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eurohunter (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 56
- Michael Halkitis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Crispulop (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
- Norman Marshall (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (167)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
- Cyclone Dikeledi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2003 LN6 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 16
- Abram Paschal Garber (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KylieTastic (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 32
- Julius Garvey (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KhaliltheHistorian985 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 24
- ¡Hasta la victoria siempre! (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SolxrgashiUnited (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
- Murder of Akiel Chambers (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Swinub (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
- Taurus TH series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SupportezLesFADH (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 16
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Shortcuts to this page: Portal:West Indies • P:CARIB
Previous Page Next Page