Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Viruses
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract involving both the stomach and small intestine, which results in diarrhoea and vomiting, and sometimes abdominal pain. It is usually caused by a virus: most commonly rotavirus and norovirus, but also adenovirus and astrovirus. Other major infectious causes include Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae and some other bacteria, as well as protozoa. Viruses, particularly rotavirus, cause about 70% of gastroenteritis episodes in children, while norovirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis among adults in America, causing over 90% of outbreaks.
Transmission can be from consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water, or by close contact with infectious individuals. Good sanitation practices and a convenient supply of uncontaminated water are important for reducing infection. Personal measures such as hand washing with soap can decrease incidence by as much as 30%. An estimated 2 billion cases of gastroenteritis occurred globally in 2015, mainly among children and people in developing countries, resulting in 1.3 million deaths. Gastroenteritis is usually an acute and self-limiting disease that does not require medication; the main treatment is rehydration using oral rehydration therapy. A rotavirus vaccine is available.
Selected image
The striping caused by tulip breaking virus, first described in 1576 by Carolus Clusius, was the second plant virus disease to be documented. The effects were much prized by 17th-century tulip growers.
Credit: Unknown (before 1640)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
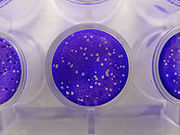
Virus quantification is necessary for viral vaccine production, and is used to manage people infected with HIV, hepatitis B and C, and cytomegalovirus. A wide range of traditional and modern methods are used. Plaque assays (pictured) infect a monolayer of host cells with dilutions of the virus and count the number of holes or plaques, where cells have lysed and infected their neighbours. For viruses that do not lyse their host cell, plaques of cells showing cytopathic effects can be counted or viral proteins can be immunostained with fluorescent-labelled antibodies. These methods quantify infectious virus, while others, such as electron microscopy, return a higher concentration because they count all virus particles, whether or not they are viable. Other assays, such as the haemagglutinin assay, quantify viral proteins.
Often slow and labour intensive, traditional methods have been complemented by modern technologies that greatly reduce quantification time, including quantitative polymerase chain reaction, flow cytometry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and tunable resistive pulse sensing.
Selected outbreak
The 1976 Zaire Ebola virus outbreak was one of the first two recorded outbreaks of the disease. The causative agent was identified as a novel virus, named for the region's Ebola River. The first identified case, in August, worked in the school in Yambuku, a small rural village in Mongala District, north Zaire. He had been treated for suspected malaria at the Yambuku Mission Hospital, which is now thought to have spread the virus by giving vitamin injections with inadequately sterilised needles, particularly to women attending prenatal clinics. Unsafe burial practices also spread the virus.
The outbreak was contained by quarantining local villages, sterilising medical equipment and providing protective clothing to medical personnel, and was over by early November. A total of 318 cases was recorded, of whom 280 died, an 88% case fatality rate. An earlier outbreak in June–November in Nzara, Sudan, was initially thought to be linked, but was shown to have been caused by a different species of Ebola virus.
Selected quotation
| “ | There are more viruses on Earth than stars in the universe. | ” |
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus, an RNA virus in the Flaviviridae family. The enveloped virion is 45–50 nm in diameter and contains a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome of around 11,000 nucleotides, encoding ten proteins. The main natural hosts are birds (the reservoir) and several species of Culex mosquito (the vector). WNV can also infect humans and some other mammals, including horses, dogs and cats, as well as some reptiles. Transmission to humans is generally by bite of the female mosquito. Mammals form a dead end for the virus, as it cannot replicate sufficiently efficiently in them to complete the cycle back to the mosquito.
First identified in Uganda in 1937, WNV was at first mainly associated with disease in horses, with only sporadic cases of human disease until the 1990s. The virus is now endemic in Africa, west and central Asia, Oceania, the Middle East, Europe and North America. A fifth of humans infected experience West Nile fever, a flu-like disease. In less than 1% of those infected, the virus invades the central nervous system, causing encephalitis, meningitis or flaccid paralysis. No specific antiviral treatment has been licensed and only a veterinary vaccine is available. Mosquito control is the main preventive measure.
Did you know?
- ...that Franquet's Epauletted Fruit Bat (pictured) is one of three fruit-eating bats found to be a reservoir for Ebola virus in the wild?
- ...that 95% of adults have been infected by human herpesvirus 7, a virus that can cause influenza-like illness and seizures but normally causes no symptoms?
- ...that James Jurin used statistical studies to show the probability of death from smallpox vaccine was significantly less than from smallpox?
- ...that the log-Cauchy distribution has been proposed as a model for the progression of HIV in individuals?
- ...that Corona, named after Corona, is fighting corona?
Selected biography
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 1920 – 16 April 1958) was a British biophysicist and X-ray crystallographer who made critical contributions to the understanding of the fine molecular structures of DNA, RNA and viruses.
Franklin led pioneering research on the structure of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), a rod-like RNA virus, using X-ray crystallography. She first showed that, contrary to contemporary opinion, TMV virus particles were all of the same length. With Kenneth Holmes, she showed the virus's coat is composed of protein molecules arranged in helices. She designed and built a model of the virus to be exhibited at the 1958 World's Fair. She speculated that the virus is hollow, and correctly hypothesized that the RNA of TMV is single-stranded. Her work, together with that of Donald Caspar, revealed that the viral RNA is wound along the inner surface of the hollow virus. Her laboratory, which also included Aaron Klug, studied other plant viruses, including turnip yellow mosaic virus and viruses infecting potato, tomato and pea. Franklin also worked on icosahedral animal viruses, including poliovirus.
Franklin is commemorated in the Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science.
In this month
February 1939: First virology journal, Archiv für die gesamte Virusforschung, appeared
8 February 1951: Establishment of the HeLa cell line from a cervical carcinoma biopsy, the first immortal human cell line
12 February 1892: Dmitri Ivanovsky (pictured) demonstrated transmission of tobacco mosaic disease by extracts filtered through Chamberland filters; sometimes considered the beginning of virology
19 February 1966: Prion disease kuru shown to be transmissible
23 February 2018: Baloxavir marboxil, the first anti-influenza agent to target the cap-dependent endonuclease activity of the viral polymerase, approved in Japan
27 February 2005: H1N1 influenza strain resistant to oseltamivir reported in a human patient
24 February 1977: Phi X 174 sequenced by Fred Sanger and coworkers, the first virus and the first DNA genome to be sequenced
28 February 1998: Publication of Andrew Wakefield's Lancet paper, subsequently discredited, linking the MMR vaccine with autism, which started the MMR vaccine controversy
Selected intervention
Zidovudine (ZDV) (also known as AZT and sold as Retrovir) is an antiretroviral drug used in the prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS. Classed as a nucleoside analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitor, it inhibits HIV's reverse transcriptase enzyme, which copies the viral RNA into DNA and is essential for its replication. The first breakthrough in AIDS therapy, ZDV was licensed in 1987. While it significantly reduces HIV replication, leading to some clinical and immunological benefits, when used alone ZDV does not completely stop replication, allowing the virus to become resistant to it. The drug is therefore used together with other anti-HIV drugs in combination therapy called highly active antiretroviral therapy. To simplify its administration, ZDV is included in combination pills with lamivudine (Combivir) and lamivudine plus abacavir (Trizivir). ZDV continues to be used to prevent HIV transmission from mother to child during childbirth; it was previously part of the standard post-exposure prophylaxis after needlestick injury.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Previous Page Next Page