Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve
| Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve | |
|---|---|
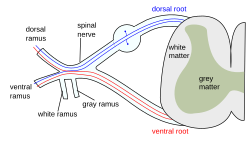 Diagram of spinal nerve | |
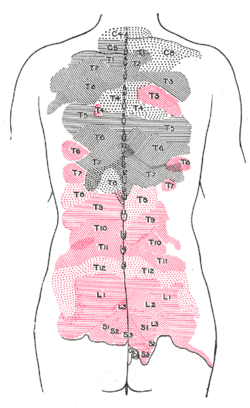 Areas of distribution of the cutaneous branches of the posterior divisions of the spinal nerves. The areas of the medial branches are in black, those of the lateral in red. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ramus posterior nervi spinalis |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.035 |
| TA2 | 6151 |
| FMA | 5983 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep (a.k.a. intrinsic or true) muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back.[1]
A spinal nerve splits within the intervertebral foramen to form a dorsal ramus and a ventral ramus. The dorsal ramus then turns to course posterior-ward before splitting into a medial branch and a lateral branch. Both these branches provide motor innervation to deep back muscles. In the neck and upper back, the medial branch is also responsible for providing sensory innervation of the skin; in the lower back, the lateral branch does so. All medial branches additionally also provide sensory innervation to the zygapophyseal joints and periosteum of the vertebral column.[1]
- ^ a b "ramus posterior nervi spinalis". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-06-13.
Previous Page Next Page


