Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Turkey
Merhaba! Türkiye portalına hoş geldiniz. Hi! Welcome to the Turkey portal.
 | |
| |
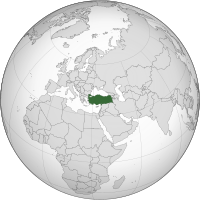
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turks, while ethnic Kurds are the largest ethnic minority. Officially a secular state, Turkey has a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city, while Istanbul is its largest city and economic and financial center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya.
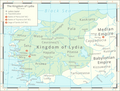
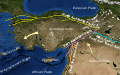
Turkey was first inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic. Home to important Neolithic sites like Göbekli Tepe and some of the earliest farming areas, present-day Turkey was inhabited by various ancient peoples. The Hattians were assimilated by the Anatolian peoples, such as the Hittites. Classical Anatolia transitioned into cultural Hellenization following the conquests of Alexander the Great; Hellenization continued during the Roman and Byzantine eras. The Seljuk Turks began migrating into Anatolia in the 11th century, starting the Turkification process. The Seljuk Sultanate of Rum ruled Anatolia until the Mongol invasion in 1243, when it disintegrated into Turkish principalities. Beginning in 1299, the Ottomans united the principalities and expanded. Mehmed II conquered Constantinople (now known as Istanbul) in 1453. During the reigns of Selim I and Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire became a global power. From 1789 onwards, the empire saw a major transformation, reforms, and centralization while its territory declined.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, persecution of Muslims during the Ottoman contraction and in the Russian Empire resulted in large-scale loss of life and mass migration into modern-day Turkey from the Balkans, Caucasus, and Crimea. Under the control of the Three Pashas, the Ottoman Empire entered World War I in 1914, during which the Ottoman government committed genocides against its Armenian, Greek, and Assyrian subjects. Following Ottoman defeat, the Turkish War of Independence resulted in the abolition of the sultanate and the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne. The Republic was proclaimed on 29 October 1923, modelled on the reforms initiated by the country's first president, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. Turkey remained neutral during most of World War II, but was involved in the Korean War. Several military interventions interfered with the transition to a multi-party system.
Turkey is an upper-middle-income and emerging country; its economy is the world's 17th-largest by nominal and 12th-largest by PPP-adjusted GDP. It is a unitary presidential republic. Turkey is a founding member of the OECD, G20, and Organization of Turkic States. With a geopolitically significant location, Turkey is a regional power and an early member of NATO. An EU candidate, Turkey is part of the EU Customs Union, CoE, OIC, and TURKSOY.
Turkey has coastal plains, a high central plateau, and various mountain ranges; its climate is temperate with harsher conditions in the interior. Home to three biodiversity hotspots, Turkey is prone to frequent earthquakes and is highly vulnerable to climate change. Turkey has a universal healthcare system, growing access to education, and increasing levels of innovativeness. It is a leading TV content exporter. With 21 UNESCO World Heritage sites, 30 UNESCO intangible cultural heritage inscriptions, and a rich and diverse cuisine, Turkey is the fifth most visited country in the world. (Full article...)
Selected article -

The Turkish economic crisis (Turkish: Türkiye ekonomik krizi) is a financial and economic crisis in Turkey. It is characterized by the Turkish lira (TRY) plunging in value, high inflation, rising borrowing costs, and correspondingly rising loan defaults. The crisis was caused by the Turkish economy's excessive current account deficit and large amounts of private foreign-currency denominated debt, in combination with President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan's increasing authoritarianism and his unorthodox ideas about interest rate policy. Some analysts also stress the leveraging effects of the geopolitical frictions with the United States. Following the detention of American pastor Andrew Brunson, who was confined of espionage charges after the failed 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt, the Trump administration exerted pressure towards Turkey by imposing further sanctions. The economic sanctions therefore doubled the tariffs on Turkey, as imported steel rises up to 50% and on aluminum to 20%. As a result, Turkish steel was priced out of the US market, which previously amounted to 13% of Turkey's total steel exports.[better source needed]
After a period of modest recovery in 2020 and early 2021 amid the COVID-19 pandemic, the Turkish lira plunged following the replacement of Central Bank chief Naci Ağbal with Şahap Kavcıoğlu, who slashed interest rates from 19% to 14%. The lira lost 44% of its value in 2021 alone. In 2023, however, Erdoğan began to follow orthodox banking methods under the guidance of Mehmet Şimşek and Hafize Gaye Erkan. The interest rate has stood at 50% since March 2024 upon the advice of Fatih Karahan, the governor of the central bank who succeeded Erkan. This contributed to the decline of inflation, since as of November 2024, inflation is at 47.09%, down from its all-time high of 83%. (Full article...)
General images
Did you know -
- ... that the crash of Turkish Airlines Flight 634 on 8 January 2003 was the worst crash involving a BAe 146? (January 4, 2009) Wikipedia:Recent additions 238
- ... that Artin Penik, a Turkish-Armenian, set himself on fire in protest of the terrorist attacks against Turks by the Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia (ASALA)? (February 25, 2007) Wikipedia:Recent additions 121
- ... that the world's longest tunnel system is the two parallel tunnels at the Atatürk Dam of Şanlıurfa in southeastern Turkey? (February 14, 2008)
- ... that modern nursing was founded by Florence Nightingale at the Selimiye Barracks in Istanbul, Turkey during the Crimean War (1854-1856)? (May 22, 2007) Wikipedia:Recent additions 142
- ... that according to US and Turkish officials, the MV Kısmetim-1 was deliberately sunk in December 1992 by its crew in order to prevent the capture of the illicit drug load? (February 1, 2009) Wikipedia:Recent additions 239
- ... that the 1955 novel Teneke by Turkish author Yaşar Kemal was adapted into an Italian |opera of the same title by Fabio Vacchi in 2007? (October 8, 2007) Wikipedia:Recent additions 175
- ... that the Battle of Shaizar in 1111, between King Baldwin I of Jerusalem's Crusader army and a Seljuk army led by Mawdud bin Altuntash of Mosul, ended in a tactical draw? (March 13, 2008) Wikipedia:Recent additions 211
Selected picture
Selected biography -
Ferit Orhan Pamuk (born 7 June 1952; Turkish pronunciation: [feˈɾit oɾˈhan paˈmuk]) is a Turkish novelist, screenwriter, academic, and recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Literature. One of Turkey's most prominent novelists, he has sold over 13 million books in 63 languages, making him the country's best-selling writer.
Pamuk's novels include Silent House, The White Castle, The Black Book, The New Life, My Name Is Red and Snow. He is the Robert Yik-Fong Tam Professor in the Humanities at Columbia University, where he teaches writing and comparative literature. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 2018. (Full article...)
Selected video -
Selected quote -
| “ | Today the Soviet Union is a friend and an ally. We need this friendship. However, no one can know what will happen tomorrow. Just like the Ottoman and Austro-Hungarian Empires it may tear itself apart or shrink in size. The people that it holds so tightly in its grip may one day slip away. The world may see a new balance of power. It is then that Turkey must know what to do. Ally Soviets have under their control our brothers with whom we share language, beliefs and roots. We must be prepared to embrace them. Being ready does not mean that we will sit quietly and wait. We must get ready. How does a people get prepared for such an endeavour? By strengthening the natural bridges that exist between us. Language is a bridge... Religion is a bridge... History is a bridge... We must delve into our roots and reconstruct what history has divided. We can't wait for them to approach us. We must reach out to them. | ” |
Recognized content
Provinces
Related portals
Religions in Turkey
Neighbouring countries
Countries with related heritage
WikiProjects
Turkish wikipedia
 |
There is a Turkish version of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. |
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Previous Page Next Page