Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
African Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone Treaty
| African Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone Treaty | |
|---|---|
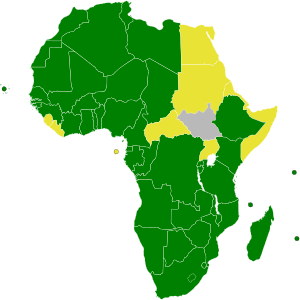 Countries that have ratified the Treaty Countries that have signed but not ratified Countries that have not signed | |
| Type | Nuclear disarmament |
| Signed | 11 April 1996 |
| Location | Cairo, Egypt |
| Effective | 15 July 2009 |
| Signatories | 53 |
| Parties | 43 |
| Depositary | OAU Secretary-General |
The African Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone Treaty, also known as the Treaty of Pelindaba (named after South Africa's main nuclear research facility, run by the South African Nuclear Energy Corporation (NECSA) and was the location where South Africa's atomic bombs of the 1970s were developed, constructed and subsequently stored),[1] establishes a Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone in Africa. The treaty was signed in 1996 and came into effect with the 28th ratification on 15 July 2009.
- ^ Von Wielligh, N. & von Wielligh-Steyn, L. (2015). The Bomb – South Africa’s Nuclear Weapons Programme. Pretoria: Litera.
Previous Page Next Page


