Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
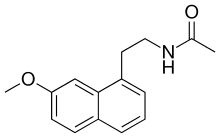
Agomelatine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Melitor, Thymanax, Valdoxan, others |
| Other names | AGO-178; AGO178C; S-20098; S-20098-F55; 7-Methoxy-N-acetyl-1-naphthylethylamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability | Low[1] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~1%[2][7] |
| Protein binding | 95%[2] |
| Metabolism | Liver (90% CYP1A2 and 10% CYP2C9)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 hours[2][7] |
| Excretion | Kidney (80%, mostly as metabolites)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.896 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 243.306 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Agomelatine, sold under the brand names Valdoxan and Thymanax, among others, is an atypical antidepressant most commonly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.[8] One review found that it is as effective as other antidepressants with similar discontinuation rates overall but fewer discontinuations due to side effects.[8][9] Another review also found it was similarly effective to many other antidepressants.[10]
Common side effects include headaches, nausea, and dizziness, which usually subside in the first few weeks, as well as liver problems[2][11] – due to the potential effect on the liver, ongoing blood tests are recommended.[12] Its use is not recommended in people with dementia, or who are under the age of 18 or over 75.[13][2] There is tentative evidence that it may have fewer side effects than some other antidepressants.[8] It acts by blocking certain serotonin receptors and activating melatonin receptors.[12]
Agomelatine was approved for medical use in Europe in 2009 and Australia in 2010.[12] Its use is not approved in the United States and efforts to get approval were ended in 2011.[12] It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Servier.[12]
- ^ Kim HK, Yang KI (December 2022). "Melatonin and melatonergic drugs in sleep disorders". Translational and Clinical Pharmacology. 30 (4): 163–171. doi:10.12793/tcp.2022.30.e21. PMC 9810491. PMID 36632077.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Valdoxan Product Information" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Servier Laboratories Pty Ltd. 2013-09-23. Archived from the original on 2017-03-24. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- ^ "Valdoxan 25 mg film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 13 July 2020. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ "Thymanax EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ "Valdoxan EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
BuoliMauriAltamura2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Guaiana G, Gupta S, Chiodo D, Davies SJ, Haederle K, Koesters M (December 2013). "Agomelatine versus other antidepressive agents for major depression". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (12): CD008851. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008851.pub2. PMC 11289707. PMID 24343836.
- ^ Taylor D, Sparshatt A, Varma S, Olofinjana O (March 2014). "Antidepressant efficacy of agomelatine: meta-analysis of published and unpublished studies". BMJ. 348: g1888. doi:10.1136/bmj.g1888. PMC 3959623. PMID 24647162.
- ^ Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Chaimani A, Atkinson LZ, Ogawa Y, et al. (April 2018). "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". Lancet. 391 (10128): 1357–1366. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32802-7. PMC 5889788. PMID 29477251.
- ^ "Summary of Product Characteristics" (PDF). European Medicine Agency. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-10-29. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- ^ a b c d e Norman TR, Olver JS (April 2019). "Agomelatine for depression: expanding the horizons?". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 20 (6): 647–656. doi:10.1080/14656566.2019.1574747. PMID 30759026. S2CID 73421269.
- ^ British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 357–358. ISBN 9780857113382.
Previous Page Next Page


