Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Arginine
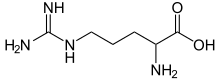 Skeletal formula of arginine
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Arginine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1725411, 1725412 D, 1725413 L | |||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.738 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 364938 D | |||
| |||
| KEGG |
| ||
| MeSH | Arginine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H14N4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 174.204 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystals | ||
| Odor | Odourless | ||
| Melting point | 260 °C; 500 °F; 533 K | ||
| Boiling point | 368 °C (694 °F; 641 K) | ||
| 14.87 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |||
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol insoluble in ethyl ether | ||
| log P | −1.652 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.18 (carboxyl), 9.09 (amino), 13.8 (guanidino) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
232.8 J K−1 mol−1 (at 23.7 °C) | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
250.6 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−624.9–−622.3 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3.7396–−3.7370 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| B05XB01 (WHO) S | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H319 | |||
| P305+P351+P338 | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
5110 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | L-Arginine | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanoic acids
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Arginine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||

Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the l-arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally.[1] Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG.[2] The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide.[3] Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid.
The one-letter symbol R was assigned to arginine for its phonetic similarity.[4]
- ^ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ IUPAC-IUBMB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". Recommendations on Organic & Biochemical Nomenclature, Symbols & Terminology etc. Archived from the original on 29 May 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-17.
- ^ Ignarro LJ (2000-09-13). Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology. Academic Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-08-052503-7.
- ^ "IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature A One-Letter Notation for Amino Acid Sequences". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 243 (13): 3557–3559. 10 July 1968. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)34176-6.
Previous Page Next Page