Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Arsenic
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allotropes | grey (most common), yellow, black (see Allotropes of arsenic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | metallic grey | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(As) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arsenic in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point | 887 K (615 °C, 1137 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | grey: 5.782 g/cm3[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 5.22 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 1090 K, 3628 kPa[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 1673 K, ? MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | grey: 24.44 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 34.76 kJ/mol (?) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 24.64 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: −3, +3, +5 −2,[5] −1,[6] 0,[7] +1,[8] +2,[9] +4[10] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 119 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 119±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 185 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
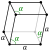
| Crystal structure | grey: rhombohedral (hR2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constants | ar = 413.15 pm α = 54.133° pm ah = 375.99 pm ch = 1054.58 pm (at 20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 5.6 µm/(m⋅K)[11] (at r.t.) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 50.2 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 333 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[12] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −5.5×10−6 cm3/mol[13] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 8 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 22 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 1440 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-38-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Arabic alchemists (before AD 815) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of arsenic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and the atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is a notoriously toxic heavy metal. It occurs naturally in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. It has various allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.
The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds.[15]
Arsenic has been known since ancient times to be poisonous to humans.[16] However, a few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic have been proposed to be an essential dietary element in rats, hamsters, goats, and chickens. Research has not been conducted to determine whether small amounts of arsenic may play a role in human metabolism.[17][18] However, arsenic poisoning occurs in multicellular life if quantities are larger than needed. Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a problem that affects millions of people across the world.
The United States' Environmental Protection Agency states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health.[19] The United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic number 1 in its 2001 prioritized list of hazardous substances at Superfund sites.[20] Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen.[19]
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Arsenic". CIAAW. 2013.
- ^ Prohaska T, Irrgeher J, Benefield J, Böhlke JK, Chesson LA, Coplen TB, Ding T, Dunn PJ, Gröning M, Holden NE, Meijer HA (4 May 2022). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b Arblaster JW (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ Gokcen, N. A (1989). "The As (arsenic) system". Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams. 10: 11–22. doi:10.1007/BF02882166.
- ^ As(−2) has been observed in CaAs; see Holleman AF, Wiberg, Egon, Wiberg, Nils (2008). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (102 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 829. ISBN 9783110206845.
- ^ As(−1) has been observed in LiAs; see Reinhard Nesper (1990). "Structure and chemical bonding in zintl-phases containing lithium". Progress in Solid State Chemistry (1): 1–45. doi:10.1016/0079-6786(90)90006-2.
- ^ Abraham MY, Wang Y, Xie Y, Wei P, Shaefer III HF, Schleyer Pv, Robinson GH (2010). "Carbene Stabilization of Diarsenic: From Hypervalency to Allotropy". Chemistry: A European Journal. 16 (2): 432–5. doi:10.1002/chem.200902840. PMID 19937872.
- ^ Ellis BD, MacDonald CL (2004). "Stabilized Arsenic(I) Iodide: A Ready Source of Arsenic Iodide Fragments and a Useful Reagent for the Generation of Clusters". Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (19): 5981–6. doi:10.1021/ic049281s. PMID 15360247.
- ^ Greenwood NN, Earnshaw A (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ As(IV) has been observed in arsenic(IV) hydroxide (As(OH)4) and HAsO−; see Kläning UK, Bielski BH, Sehested K (1989). "Arsenic(IV). A pulse-radiolysis study". Inorganic Chemistry. 28 (14): 2717–24. doi:10.1021/ic00313a007.
- ^ Cverna, Fran (2002). ASM Ready Reference: Thermal properties of metals. ASM International. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-0-87170-768-0. pdf.
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2000). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (81 ed.). CRC press. ISBN 0849304814.
- ^ Weast R (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Kondev FG, Wang M, Huang WJ, Naimi S, Audi G (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ Grund, Sabina C., Hanusch, Kunibert, Wolf, Hans Uwe. "Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ "Arsenic: A Murderous History | Dartmouth Toxic Metals".
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ANutwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
UEssentwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Dibyendu S, Datta R (2007). "Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- ^ Carelton J (2007). "Final Report: Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". United States Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
Previous Page Next Page