Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
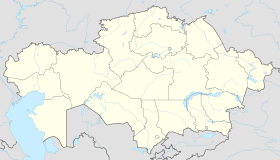
Baikonur
Baikonur
| |
|---|---|
An aerial view of Baikonur | |
|
| |
 | |
| Coordinates: 45°37′0″N 63°19′0″E / 45.61667°N 63.31667°E | |
| Country | Kazakhstan Russia (administered) |
| Founded | 1955 |
| Incorporated (city) | 1966 |
| Government | |
| • Administrator | Konstantin Dmitrievich Busygin |
| Area | |
• Total | 57 km2 (22 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 100 m (300 ft) |
| Population (2020)[1] | |
• Total | 39,341 |
| • Density | 690/km2 (1,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:00[2] |
| Postal code | 710501 |
| Area code | +7 73622 |
| Vehicle registration | N, 11 (Kazakhstan), 94 (Russia) |
| Climate | BWk |
| Website | www |
Baikonur (Russian: Байконур [bəjkɐˈnur]; Kazakh: Байқоңыр, romanized: Baiqoñyr [bɑjqoˈŋɤr]) is a city in Kazakhstan on the northern bank of the Syr Darya river. It is currently leased and administered by the Russian Federation as an enclave until 2050.[3] It was constructed to serve the Baikonur Cosmodrome with administrative offices and employee housing. During the Soviet period, the town was known as Leninsk, and was sometimes referred to as Zvezdograd (Russian: Звездоград, lit. 'Star City').[4] It was officially renamed Baikonur by Russian president Boris Yeltsin on December 20, 1995.
The Russian controlled area is an ellipse measuring 90 kilometres (56 mi) east to west by 85 km (53 mi) north to south, with the cosmodrome situated at the area's centre.
Foreign visitors and tourists can visit the cosmodrome and city but need to obtain a specific permit from Roscosmos.[5]
- ^ "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года" (PDF). Комитет по статистике Министерства национальной экономики Республики Казахстан. Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ On the time change in the city of Baikonur and Kyzylorda region, Administration of the city of Baikonur, 13 December 2018 (in Russian).
- ^ "Kazakhstan: Russia to keep using Baikonur until at least 2050 | Eurasianet".
- ^ Barensky, C.; Lardier, Stefan (2013). The Soyuz launch vehicle the two lives of an engineering triumph. New York: Springer. p. 189. ISBN 978-1461454595.
- ^ "British YouTube travel star Benjamin Rich arrested at Baikonur Cosmodrome, Russia says". Reuters. 2022-05-08. Retrieved 2023-09-02.
Previous Page Next Page