Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Bone remodeling
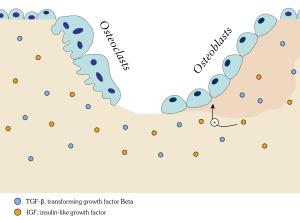
In osteology, bone remodeling or bone metabolism is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton (a process called bone resorption) and new bone tissue is formed (a process called ossification or new bone formation). Recent research has identified a specialised subset of blood vessels, termed Type R endothelial cells, in the bone microenvironment.[1] These blood vessels play a crucial role in adult bone remodelling by mediating interactions between bone-resorbing osteoclasts and bone-forming osteoblasts. Type R blood vessels are characterised by their association with post-arterial capillaries and exhibit unique remodelling properties crucial for bone homeostasis.[2] These processes also control the reshaping or replacement of bone following injuries like fractures but also micro-damage, which occurs during normal activity. Remodeling responds also to functional demands of the mechanical loading.
In the first year of life, almost 100% of the skeleton is replaced. In adults, remodeling proceeds at about 10% per year.[3]
An imbalance in the regulation of bone remodeling's two sub-processes, bone resorption and bone formation, results in many metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis.[4]
- ^ Mohanakrishnan, Vishal; Sivaraj, Kishor K.; Jeong, Hyun-Woo; Bovay, Esther; Dharmalingam, Backialakshmi; Bixel, M. Gabriele; Dinh, Van Vuong; Petkova, Milena; Paredes Ugarte, Isidora; Kuo, Yi-Tong; Gurusamy, Malarvizhi; Raftrey, Brian; Chu, Nelson Tsz Long; Das, Soumyashree; Rios Coronado, Pamela E.; Stehling, Martin; Sävendahl, Lars; Chagin, Andrei S.; Mäkinen, Taija; Red-Horse, Kristy; Adams, Ralf H. (2024). "Specialized post-arterial capillaries facilitate adult bone remodelling". Nature. 26 (12): 2020–2034. doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01545-1. PMID 39528700.
- ^ Mohanakrishnan, Vishal; Sivaraj, Kishor K.; Jeong, Hyun-Woo; Bovay, Esther; Dharmalingam, Backialakshmi; Bixel, M. Gabriele; Dinh, Van Vuong; Petkova, Milena; Paredes Ugarte, Isidora; Kuo, Yi-Tong; Gurusamy, Malarvizhi; Raftrey, Brian; Chu, Nelson Tsz Long; Das, Soumyashree; Rios Coronado, Pamela E.; Stehling, Martin; Sävendahl, Lars; Chagin, Andrei S.; Mäkinen, Taija; Red-Horse, Kristy; Adams, Ralf H. (2024). "Specialized post-arterial capillaries facilitate adult bone remodelling". Nature. 26 (12): 2020–2034. doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01545-1. PMID 39528700.
- ^ "Wheeless Textbook". 22 July 2020.
- ^ Online Medical Dictionary.
Previous Page Next Page


