Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Cerebroside
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2014) |
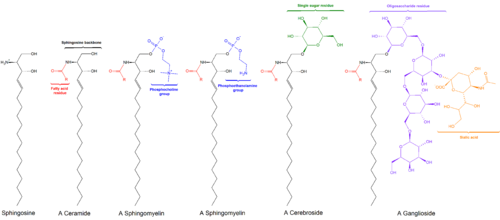
Cerebrosides (monoglycosylceramides) are a group of glycosphingolipids which are important components of animal muscle and nerve cell membranes.
They consist of a ceramide with a single sugar residue at the 1-hydroxyl moiety. The sugar residue can be either glucose or galactose; the two major types are therefore called glucocerebrosides (a.k.a. glucosylceramides) and galactocerebrosides (a.k.a. galactosylceramides). Galactocerebrosides are typically found in neural tissue, while glucocerebrosides are found in other tissues.
Previous Page Next Page


