Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Chilas
Chilas
چلاس | |
|---|---|
City administered by Pakistan | |
 The Indus River near Chilas | |
 Interactive map of Chilas | |
![A map showing Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan shaded in sage-green colour in the disputed Kashmir region[1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/84/Kashmir_region._LOC_2003626427_-_showing_sub-regions_administered_by_different_countries.jpg/250px-Kashmir_region._LOC_2003626427_-_showing_sub-regions_administered_by_different_countries.jpg) A map showing Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan shaded in sage-green colour in the disputed Kashmir region[1] | |
| Coordinates: 35°25′10″N 74°05′40″E / 35.41944°N 74.09444°E | |
| Administering country | Pakistan |
| Autonomous state | Gilgit-Baltistan |
| District | Diamer District |
| Elevation | 1,265 m (4,150 ft) |
| Population (2017-2017) | |
• Total | 214,000 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Urdu, Shina[2] |
| Time zone | UTC+5 (PST) |
| PIN | 14100 – 1xx[3] |
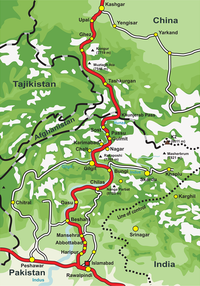
Chilas (Urdu: چلاس) is a city in Pakistani-administered Gilgit–Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region.[1] It is the divisional capital of Diamer Division and is located on the Indus River. It is part of the Silk Road, connected by the Karakoram Highway and N-90 National Highway to Islamabad and Peshawar in the southwest, via Hazara and Malakand divisions of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. To the north, Chilas connects to the cities of Tashkurgan and Kashgar in Xinjiang, China, via Gilgit, Aliabad, Sust, and the Khunjerab Pass.
Chilas is the headquarters of Diamir district.[4] The weather is hot and dry in the summer and dry and cold in the winter. It can be reached by the Karakoram highway and also through the Kaghan valley and the Babusar Pass. Chilas is on the left bank of the Indus River. The beautiful Fairy Meadows National Park and Nanga Parbat, the ninth highest peak in the world, are also located in Chilas.
Karakoram International University recently opened a sub-campus in Chilas.
- ^ a b The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the tertiary sources (a) through (d), reflecting due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (f) through (h) below, "held" is also considered politicized usage, as is the term "occupied," (see (i) below).
(a) Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, the last two being part of a territory called the Northern Areas. Administered by India are the southern and southeastern portions, which constitute the state of Jammu and Kashmir but are slated to be split into two union territories.";
(b) Pletcher, Kenneth, Aksai Chin, Plateau Region, Asia, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 16 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "Aksai Chin, Chinese (Pinyin) Aksayqin, portion of the Kashmir region, at the northernmost extent of the Indian subcontinent in south-central Asia. It constitutes nearly all the territory of the Chinese-administered sector of Kashmir that is claimed by India to be part of the Ladakh area of Jammu and Kashmir state.";
(c) "Kashmir", Encyclopedia Americana, Scholastic Library Publishing, 2006, p. 328, ISBN 978-0-7172-0139-6 C. E Bosworth, University of Manchester Quote: "KASHMIR, kash'mer, the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent, administered partlv by India, partly by Pakistan, and partly by China. The region has been the subject of a bitter dispute between India and Pakistan since they became independent in 1947";
(d) Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003), Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M, Taylor & Francis, pp. 1191–, ISBN 978-0-415-93922-5 Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute betw een India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China."
(e) Talbot, Ian (2016), A History of Modern South Asia: Politics, States, Diasporas, Yale University Press, pp. 28–29, ISBN 978-0-300-19694-8 Quote: "We move from a disputed international border to a dotted line on the map that represents a military border not recognized in international law. The line of control separates the Indian and Pakistani administered areas of the former Princely State of Jammu and Kashmir.";
(f) Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent, Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "... China became active in the eastern area of Kashmir in the 1950s and has controlled the northeastern part of Ladakh (the easternmost portion of the region) since 1962.";
(g) Bose, Sumantra (2009), Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace, Harvard University Press, pp. 294, 291, 293, ISBN 978-0-674-02855-5 Quote: "J&K: Jammu and Kashmir. The former princely state that is the subject of the Kashmir dispute. Besides IJK (Indian-controlled Jammu and Kashmir. The larger and more populous part of the former princely state. It has a population of slightly over 10 million, and comprises three regions: Kashmir Valley, Jammu, and Ladakh.) and AJK ('Azad" (Free) Jammu and Kashmir. The more populous part of Pakistani-controlled J&K, with a population of approximately 2.5 million. AJK has six districts: Muzaffarabad, Mirpur, Bagh, Kodi, Rawalakot, and Poonch. Its capital is the town of Muzaffarabad. AJK has its own institutions, but its political life is heavily controlled by Pakistani authorities, especially the military), it includes the sparsely populated "Northern Areas" of Gilgit and Baltistan, remote mountainous regions which are directly administered, unlike AJK, by the Pakistani central authorities, and some high-altitude uninhabitable tracts under Chinese control."
(h) Fisher, Michael H. (2018), An Environmental History of India: From Earliest Times to the Twenty-First Century, Cambridge University Press, p. 166, ISBN 978-1-107-11162-2 Quote: "Kashmir’s identity remains hotly disputed with a UN-supervised “Line of Control” still separating Pakistani-held Azad (“Free”) Kashmir from Indian-held Kashmir.";
(i) Snedden, Christopher (2015), Understanding Kashmir and Kashmiris, Oxford University Press, p. 10, ISBN 978-1-84904-621-3 Quote:"Some politicised terms also are used to describe parts of J&K. These terms include the words 'occupied' and 'held'." - ^ "INDO-IRANIAN FRONTIER LANGUAGES". Encyclopaedia Iranica. 15 November 2006. Retrieved 2015-11-06.
- ^ "Post Codes". Pakistan Post Office. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ^ Pamir Times August 2, 2012
Previous Page Next Page


