Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Chlorine azide
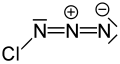 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorine azide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| ClN3 | |||
| Molar mass | 77.4731 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Yellow-orange liquid; colorless gas | ||
| Melting point | −100 °C (−148 °F; 173 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) | ||
| Solubility | Soluble[vague] in butane, pentane, benzene, methanol, ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and carbon disulfide; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Structure | |||
| orthorhombic | |||
| Cmc 21, No. 36[1] | |||
| Explosive data | |||
| Shock sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Friction sensitivity | Extreme | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Extremely sensitive explosive | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Hydrazoic acid Fluorine azide Bromine azide Iodine azide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Chlorine azide (ClN3) is an inorganic compound that was discovered in 1908 by Friedrich Raschig.[2] Concentrated ClN3 is notoriously unstable and may spontaneously detonate at any temperature.[3]
- ^ Lyhs, Benjamin; Bläser, Dieter; Wölper, Christoph; Schulz, Stephan; Jansen, Georg (2012). "A Comparison of the Solid-State Structures of Halogen Azides XN3 (X=Cl, Br, I)". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 51 (51): 12859–12863. doi:10.1002/anie.201206028. PMID 23143850.
- ^ Frierson, W. J.; Browne, A. W. (1943). "Chlorine Azide. II. Interaction of Chlorine Azide and Silver Azide. Azino Silver Chloride, N3AgCl". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 65 (9): 1698–1700. Bibcode:1943JAChS..65.1698F. doi:10.1021/ja01249a013.
- ^ Frierson, W. J.; Kronrad, J.; Browne, A. W. (1943). "Chlorine Azide, ClN3. I.". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 65 (9): 1696–1698. Bibcode:1943JAChS..65.1696F. doi:10.1021/ja01249a012.
Previous Page Next Page





