Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
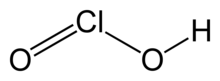
Chlorous acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorous acid, Chloric (III) acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H Cl O2 | |
| Molar mass | 68.46 g/mol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.96 |
| Conjugate base | Chlorite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the formula HClO2. It is a weak acid. Chlorine has oxidation state +3 in this acid. The pure substance is unstable, disproportionating to hypochlorous acid (Cl oxidation state +1) and chloric acid (Cl oxidation state +5):
- 2 HClO2 → HClO + HClO3
Although the acid is difficult to obtain in pure substance, the conjugate base, chlorite, derived from this acid is stable. One example of a salt of this anion is the well-known sodium chlorite. This and related salts are sometimes used in the production of chlorine dioxide.
Previous Page Next Page


