Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis
| Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis | |
|---|---|
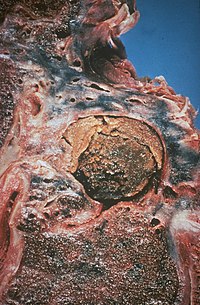 | |
| An example of aspergilloma, one form of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis, following tuberculosis. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Weight loss, cough, shortness of breath, haemoptysis, fatigue, malaise, chest pain, sputum production, fever[1] |
| Risk factors | Underlying respiratory disease,[2] genetic defects[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Via imaging (chest X-ray, high resolution CT scanning)[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Lung cancer, tuberculosis, other fungal infections[5] |
| Treatment | Antifungal medications (oral or intravenous),[6][7] surgery,[6] glucocorticoids[8] |
| Prognosis | Approximately 20-40% mortality at 3 years; 50-80% at 7-10 years[9][10][11] |
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis is a long-term fungal infection caused by members of the genus Aspergillus—most commonly Aspergillus fumigatus.[8] The term describes several disease presentations with considerable overlap, ranging from an aspergilloma[12]—a clump of Aspergillus mold in the lungs—through to a subacute, invasive form known as chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis which affects people whose immune system is weakened. Many people affected by chronic pulmonary aspergillosis have an underlying lung disease, most commonly tuberculosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, asthma, or lung cancer.[8]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Denning_2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Smith NL, Denning DW (April 2011). "Underlying conditions in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis including simple aspergilloma". The European Respiratory Journal. 37 (4): 865–72. doi:10.1183/09031936.00054810. PMID 20595150.
- ^ Carvalho A, Pasqualotto AC, Pitzurra L, Romani L, Denning DW, Rodrigues F (February 2008). "Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor genes and susceptibility to pulmonary aspergillosis". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 197 (4): 618–21. doi:10.1086/526500. hdl:1822/61456. PMID 18275280.
- ^ Desai SR, Hedayati V, Patel K, Hansell DM (October 2015). "Chronic Aspergillosis of the Lungs: Unravelling the Terminology and Radiology". European Radiology. 25 (10): 3100–7. doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3690-7. PMID 25791639. S2CID 13065490.
- ^ Kim SH, Kim MY, Hong SI, Jung J, Lee HJ, Yun SC, et al. (July 2015). "Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis-mimicking Tuberculosis". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 61 (1): 9–17. doi:10.1093/cid/civ216. PMID 25778752.
- ^ a b Denning DW, Cadranel J, Beigelman-Aubry C, Ader F, Chakrabarti A, Blot S, et al. (January 2016). "Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: rationale and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management". The European Respiratory Journal. 47 (1): 45–68. doi:10.1183/13993003.00583-2015. PMID 26699723.
- ^ Patterson TF, Thompson GR, Denning DW, Fishman JA, Hadley S, Herbrecht R, et al. (August 2016). "Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 63 (4): e1 – e60. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw326. PMC 4967602. PMID 27365388.
- ^ a b c Denning DW. "Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis". www.uptodate.com. UpToDate. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Lowes D, Al-Shair K, Newton PJ, Morris J, Harris C, Rautemaa-Richardson R, Denning DW (February 2017). "Predictors of mortality in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis". The European Respiratory Journal. 49 (2): 1601062. doi:10.1183/13993003.01062-2016. PMID 28179437.
- ^ Tomlinson JR, Sahn SA (September 1987). "Aspergilloma in sarcoid and tuberculosis". Chest. 92 (3): 505–8. doi:10.1378/chest.92.3.505. PMID 3622028.
- ^ Ohba H, Miwa S, Shirai M, Kanai M, Eifuku T, Suda T, et al. (May 2012). "Clinical characteristics and prognosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis". Respiratory Medicine. 106 (5): 724–9. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2012.01.014. PMID 22349065.
- ^ Judson MA, Stevens DA (October 2001). "The treatment of pulmonary aspergilloma". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 2 (10): 1375–7. PMID 11890350.
Previous Page Next Page


