Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Direct Media Interface
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2014) |
| Direct Media Interface | |
| Created by | Intel |
|---|---|
| Supersedes | Intel Hub Architecture |
| Speed |
|
| Style | Serial |
In computing, Direct Media Interface (DMI) is Intel's proprietary link between the northbridge (or CPU) and southbridge (e.g. Platform Controller Hub family) chipset on a computer motherboard.[1] It was first used between the 9xx chipsets and the ICH6, released in 2004.[2]: 1 Previous Intel chipsets had used the Intel Hub Architecture to perform the same function, and server chipsets use a similar interface called Enterprise Southbridge Interface (ESI).[3] While the "DMI" name dates back to ICH6, Intel mandates specific combinations of compatible devices, so the presence of a DMI does not guarantee by itself that a particular northbridge–southbridge combination is allowed.
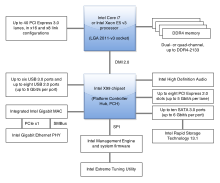
DMI is essentially PCI Express, using multiple lanes and differential signaling to form a point-to-point link. Most implementations use a ×8 or ×4 link, while some mobile systems (e.g. 915GMS, 945GMS/GSE/GU and the Atom N450) use a ×2 link, halving the bandwidth. The original implementation provides 10 Gbit/s (1 GB/s) in each direction using a ×4 link. The DMI provides support for concurrent traffic and isochronous data transfer capabilities.[2]: 3 [4]
DMI replaced FSB (Front Side Bus) which was eliminated in 2009.[5]
- ^ "What Is the Direct Media Interface (DMI) of Intel Processors?". Intel. Retrieved 2023-06-05.
- ^ a b "Second-Generation Intel Centrino TM Mobile Technology" (PDF). Intel Technology Journal. 9 (1). February 17, 2005. doi:10.1535/itj.0901. ISSN 1535-864X.
- ^ "Intel 5520 Chipset and Intel 5500 Chipset Datasheet" (PDF). Intel. March 2009. Retrieved 2014-11-06.
- ^ "Direct Media Interface (DMI) - 1.0 - ID:721073 | Intel NUC 12 Extreme / Pro X". edc.intel.com. Retrieved 2023-06-05.
- ^ "Core i7 975 review (Page 4)". 2 June 2009.
Previous Page Next Page
Direct Media Interface Czech Direct Media Interface German Direct Media Interface French Direct Media Interface Italian Direct Media Interface Japanese 다이렉트 미디어 인터페이스 Korean Direct Media Interface Polish Direct Media Interface Portuguese Direct Media Interface Russian Direct Media Interface Ukrainian


