Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Echinostoma revolutum
| Echinostoma revolutum | |
|---|---|
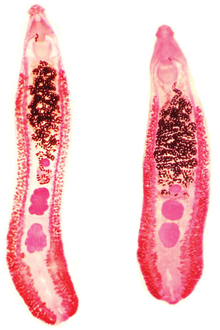
| |
| Two specimens of Echinostoma revolutum, from:[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Order: | Plagiorchiida |
| Family: | Echinostomatidae |
| Genus: | Echinostoma |
| Species: | E. revolutum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Echinostoma revolutum (Fröhlich, 1802) Looss, 1899
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Echinostoma revolutum is a trematode parasite of which the adults can infect birds and mammals, including humans. In humans, it causes echinostomiasis.[1]
- ^ a b Sohn, Woon-Mok; Chai, Jong-Yil; Yong, Tai-Soon; Eom, Keeseon S.; Yoon, Cheong-Ha; Sinuon, Muth; Socheat, Duong; Lee, Soon-Hyung (2011). "Echinostoma revolutumInfection in Children, Pursat Province, Cambodia". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 17 (1): 117–9. doi:10.3201/eid1701.100920. PMC 3204640. PMID 21192870..
- ^ Chai, Jong-Yil; Cho, Jaeeun; Chang, Taehee; Jung, Bong-Kwang; Sohn, Woon-Mok (2020). "Taxonomy of Echinostoma revolutum and 37-collar-spined Echinostoma spp.: A historical review". The Korean Journal of Parasitology. 58 (4): 343–371. doi:10.3347/kjp.2020.58.4.343. PMC 7462802. PMID 32871630.
Previous Page Next Page


