Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Edema
| Edema | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oedema, œdema, fluid retention, water retention, dropsy, hydropsy |
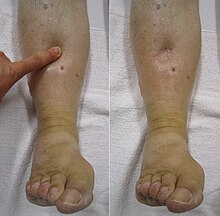 | |
| "Pitting" edema | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Cardiology, nephrology |
| Symptoms | Skin which feels tight, area may feel heavy[1] |
| Usual onset | Sudden or gradual[2] |
| Types | Generalized, localized[2] |
| Causes | Venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, lymphedema[1][2] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on a physical exam[3] |
| Treatment | Based on cause[2] |
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue,[1] a type of swelling.[4] Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected.[1] Symptoms may include skin that feels tight, the area feeling heavy, and joint stiffness.[1] Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause.[2]
Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, kwashiorkor, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema.[1][2] It may also occur in immobile patients (stroke, spinal cord injury, aging), or with temporary immobility such as prolonged sitting or standing, and during menstruation or pregnancy.[1] The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present.[2]
Treatment depends on the underlying cause.[2] If the underlying mechanism involves sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used.[2] Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful for edema of the legs.[3] Older people are more commonly affected.[3] The word is from the Ancient Greek οἴδημα oídēma meaning 'swelling'.[5]
- ^ a b c d e f g Causes and signs of edema. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Edema - Cardiovascular Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- ^ a b c "Edema: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment". Family doctor. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
- ^ Creason C (2010-11-04). Stedman's Medical Terminology: Steps to Success in Medical Language. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-58255-816-5.
- ^ Liddell H. "οἴδ-ημα". A Greek-English Lexicon. Tufts. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
Previous Page Next Page


