Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Environmental health
| Part of a series on |
| Public health |
|---|
 |
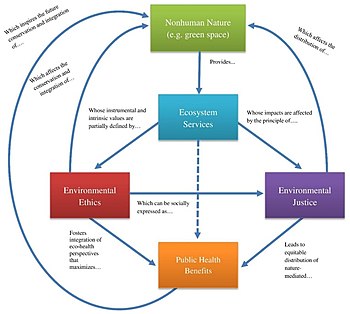

Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment affecting human health. To effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements that must be met to create a healthy environment must be determined.[1] The major sub-disciplines of environmental health are environmental science, toxicology, environmental epidemiology, and environmental and occupational medicine.[2]
- ^ Dovjak, Mateja; Kukec, Andreja (2019), "Health Outcomes Related to Built Environments", Creating Healthy and Sustainable Buildings, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 43–82, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-19412-3_2, ISBN 978-3-030-19411-6, S2CID 190160283
- ^ Kelley, Timothy (2008-07-21). "The ecology of environmental health". Environmental Health Insights. 2: 25–26. Bibcode:2008EnvHI...200200K. doi:10.1177/117863020800200001. ISSN 1178-6302. PMC 3091335. PMID 21572828.
Previous Page Next Page


