Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
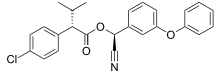
Esfenvalerate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(S)-Cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl (2S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutanoate | |
| Other names
Asana
(S)-Fenvalerate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 4275674 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.804 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3349 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H22ClNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 419.91 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.211 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 60 °C (140 °F; 333 K) |
| log P | 6.22 |
| Vapor pressure | 0 mmHg at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H313, H316, H317, H320, H330, H335, H370, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P307+P311, P310, P312, P314, P320, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 256 °C (493 °F; 529 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide marketed under the brand Asana.[2] It is the (S)-enantiomer of fenvalerate.[3]
In the United States, a limit of .05 ppm of the chemical's residue is permissible in food.[4]
- ^ Kelly, Kevin. "Environmental Fate of Esfenvalerate". California Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ^ Fishel, Frederick M. (2012). "Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Synthetic Pyrethroid Pesticides". University of Florida. Archived from the original on May 12, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ^ "Esfenvalerate". EXTONET (Extension Toxicology Network). Cooperative Extension Offices of Cornell University, Michigan State University, Oregon State University, and University of California at Davis. May 1994. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ^ The Code of Federal Regulations of the United States of America. U.S. Government Printing Office. 2006. pp. 445–446.
Previous Page Next Page


