Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
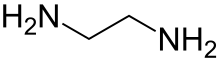
Ethylenediamine
 | |||
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethane-1,2-diamine[2] | |||
| Other names
Edamine,[1] 1,2-Diaminoethane, 'en' when a ligand
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | en | ||
| 605263 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.154 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1098 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | ethylenediamine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1604 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H8N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 60.100 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[3] | ||
| Odor | Ammoniacal[3] | ||
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3[3] | ||
| Melting point | 8 °C (46 °F; 281 K)[3] | ||
| Boiling point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K)[3] | ||
| miscible | |||
| log P | −2.057 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1.3 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
5.8 mol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4565 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
172.59 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
202.42 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−63.55 to −62.47 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1.8678 to −1.8668 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H226, H302, H311, H314, H317, H332, H334, H412 | |||
| P101, P102, P260, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K)[3] | ||
| 385 °C (725 °F; 658 K)[3] | |||
| Explosive limits | 2.7–16% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
500 mg/kg (oral, rat) 470 mg/kg (oral, guinea pig) 1160 mg/kg (oral, rat)[5] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3)[4] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3)[4] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1000 ppm[4] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanamines
|
1,2-Diaminopropane, 1,3-Diaminopropane | ||
Related compounds
|
Ethylamine, Ethylenedinitramine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998.[6] Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines.
- ^ "32007R0129". European Union. 12 February 2007. Annex II. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 676. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0269". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Ethylenediamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut (2005). "Amines, Aliphatic". Amines, Aliphatic. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.
Previous Page Next Page





