Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Fermi gas
| Condensed matter physics |
|---|
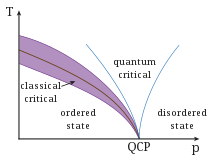 |
A Fermi gas is an idealized model, an ensemble of many non-interacting fermions. Fermions are particles that obey Fermi–Dirac statistics, like electrons, protons, and neutrons, and, in general, particles with half-integer spin. These statistics determine the energy distribution of fermions in a Fermi gas in thermal equilibrium, and is characterized by their number density, temperature, and the set of available energy states. The model is named after the Italian physicist Enrico Fermi.[1][2]
This physical model is useful for certain systems with many fermions. Some key examples are the behaviour of charge carriers in a metal, nucleons in an atomic nucleus, neutrons in a neutron star, and electrons in a white dwarf.
- ^ Fermi, Enrico (1926-11-01). "Zur Quantelung des idealen einatomigen Gases" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Physik (in German). 36 (11–12): 902–912. Bibcode:1926ZPhy...36..902F. doi:10.1007/BF01400221. ISSN 0044-3328. S2CID 123334672. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-04-06.
- ^ Zannoni, Alberto (1999). "On the Quantization of the Monoatomic Ideal Gas". arXiv:cond-mat/9912229.
An english translation of the original work of Enrico Fermi on the quantization of the monoatomic ideal gas, is given in this paper
Previous Page Next Page


