Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
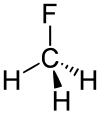
Fluoromethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Fluoromethane
| |||
| Other names
Freon 41
Methyl fluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | R41 | ||
| 1730725 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.907 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 391 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Fluoromethane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | UN 2454 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3F | |||
| Molar mass | 34.03 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Odor | pleasant, ether-like odour at high concentrations | ||
| Density | 1.4397 g/L 0.557 g/cm3 (liquid) at saturation pressure at 25 °C | ||
| Melting point | −137.8 °C (−216.0 °F; 135.3 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | −78.4 °C (−109.1 °F; 194.8 K)[1] | ||
| 1.66 L/kg (2.295 g/L) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 3.3 MPa | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220 | |||
| P210, P377, P381, P403, P410+P403 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is made of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. The name stems from the fact that it is methane (CH4) with a fluorine atom substituted for one of the hydrogen atoms. It is used in semiconductor manufacturing processes as an etching gas in plasma etch reactors.[2]
Fluoromethane (originally called "fluorohydrate of methylene") became the first organofluorine compound to be discovered[3] when it was synthesized by French chemists Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot in 1835 by distilling dimethyl sulfate with potassium fluoride.[4]
- ^ a b Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ Siegemund, Günter; Schwertfeger, Werner; Feiring, Andrew; Smart, Bruce; Behr, Fred; Vogel, Herward; McKusick, Blaine (2002). "Fluorine Compounds, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Okazoe, Takashi (2009). "Overview on the history of organofluorine chemistry from the viewpoint of material industry". Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B. 85 (8): 276–289. Bibcode:2009PJAB...85..276O. doi:10.2183/pjab.85.276. PMC 3621566. PMID 19838009.
- ^ Crochard (París); Arago, François; Gay-Lussac, Joseph Louis (1835). Annales de chimie et de physique (in French). Chez Crochard. p. 36.
Previous Page Next Page