Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Immunoglobulin heavy chain
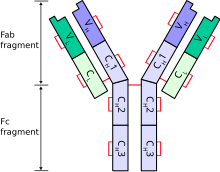

The immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) is the large polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). In human genome, the IgH gene loci are on chromosome 14.
A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains. Several different types of heavy chain exist that define the class or isotype of an antibody. These heavy chain types vary between different animals. All heavy chains contain a series of immunoglobulin domains, usually with one variable domain (VH) that is important for binding antigen and several constant domains (CH1, CH2, etc.). Production of a viable heavy chain is a key step in B cell maturation. If the heavy chain is able to bind to a surrogate light chain and move to the plasma membrane, then the developing B cell can begin producing its light chain.[2]
The heavy chain does not always have to bind to a light chain. Pre-B lymphocytes can synthesize heavy chain in the absence of light chain, which then can allow the heavy chain to bind to a heavy-chain binding protein.[3]
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on April 19, 2007. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)[full citation needed] - ^ Mårtensson, I-L; Ceredig, R (2017-01-23). "Role of the surrogate light chain and the pre-B-cell receptor in mouse B-cell development". Immunology. 101 (4): 435–441. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00151.x. ISSN 0019-2805. PMC 2327112. PMID 11122446.
- ^ Haas, Ingrid G.; Wabl, Matthias (1983). "Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein". Nature. 306 (5941): 387–9. Bibcode:1983Natur.306..387H. doi:10.1038/306387a0. PMID 6417546. S2CID 4247626.
Previous Page Next Page


