Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Massina Empire
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
Caliphate of Hamdullahi خلافة حمد الله | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1818–1862 | |||||||||||
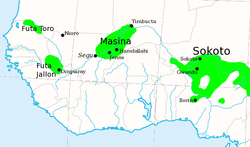 The Fulani Jihad States of West Africa, c. 1830. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Hamdullahi | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Maasina Fulfulde(Official) | ||||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||||
| Government | Caliphate | ||||||||||
| Almami | |||||||||||
• 1818 – 1845 | Seku Amadu | ||||||||||
• 1845 – 1852 | Amadu II | ||||||||||
• 1852 – 1862 | Amadu III | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Grand Council | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Late modern period; Fula jihads | ||||||||||
• Founding of the Sultanate of Massina | c. 1400 | ||||||||||
• Battle of Noukouma | 1818 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1862 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Mali | ||||||||||
The Caliphate of Hamdullahi (Arabic: خلافة حمد الله; Fula: Laamorde Maasina; Bambara: Massina Mansamara; French: Empire du Macina; also: Dina of Massina, Sise Jihad state), commonly known as the Massina empire (also spelled Maasina or Macina), was an early nineteenth-century Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa centered in the Inner Niger Delta of what is now the Mopti and Ségou Regions of Mali. It was founded by Seku Amadu in 1818 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Bambara Empire and its allies at the Battle of Noukouma. By 1853, the empire had fallen into decline and was ultimately destroyed by Omar Saidou Tall of Toucouleur.[1]
The Massina Empire was one of the most organized theocratic states of its time on the African continent and had its capital at Hamdullahi. It was ruled by an almami with the help of a Grand Council that possessed the power to elect new rulers after the death of the previous one.[1] While, in theory, the almami did not have to be a member of the Bari family, but only someone who was learned and pious, every almami elected happened to be a son of the previous ruler.[2]
- ^ a b Brodnicka, Monika (11 January 2016). "Massina Empire". The Encyclopedia of Empire. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 1–3. doi:10.1002/9781118455074.wbeoe388. ISBN 978-1-118-44064-3.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page


