Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Methylococcus capsulatus
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
| Methylococcus capsulatus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Pseudomonadota |
| Class: | Gammaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Methylococcales |
| Family: | Methylococcaceae |
| Genus: | Methylococcus |
| Species: | M. capsulatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Methylococcus capsulatus Foster and Davis 1966 (Approved Lists 1980)
| |
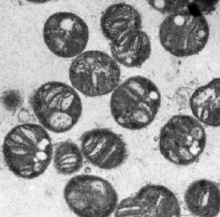
Methylococcus capsulatus is an obligately methanotrophic gram-negative, non-motile coccoid bacterium. M. capsulatus are thermotolerant; their cells are encapsulated and tend to have a diplococcoid shape. The cell wall is composed of three layers: outer membrane, peptidoglycan layer, and inner membrane. There are extensive intracytoplasmic membranes that are believed to be formed by invaginations of the inner cell membrane. More of these intracytoplasmic membranes are produced when M. capsulatus is grown at a high copper-to-biomass ratio. In addition to methane, M. capsulatus is able to oxidize some organic hydrogen containing compounds such as methanol. It has been used commercially to produce animal feed from natural gas.[1][2][3]
- ^ "Methylococcus capsulatus - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Norferm2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
LePage2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page


