Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Monarch butterfly migration

Piedra Herrada, Mexico

Piedra Herrada, Mexico
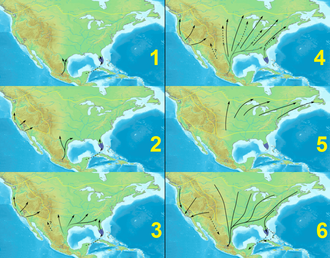
Monarch butterfly migration is the phenomenon, mainly across North America, where the subspecies Danaus plexippus plexippus migrates each autumn to overwintering sites on the West Coast of California or mountainous sites in Central Mexico. Other populations from around the world perform minor migrations or none at all. This massive movement of butterflies has been recognized as "one of the most spectacular natural phenomena in the world".[1]
The North American monarchs begin their southern migration in September and October. Migratory monarchs originate in southern Canada and the northern United States, they travel thousands of kilometers to overwintering sites in central Mexico. The butterflies arrive at their roosting sites in November. They remain in roosts atop volcanic mountains on oyamel fir trees (Abies religiosa) during the winter months and then begin their northern migration in March, back to North America and southern Canada. Two to three generations of monarchs complete the migration north. Female monarchs lay eggs for a subsequent generation during the northward migration.[2] Four generations are involved in the annual cycle and the generation undertaking the southbound migration live eight times longer than their parents and grandparents due to regulating an age-inducing hormone.[3]
Similarly, the western populations migrate annually from regions west of the Rocky Mountains to overwintering sites on the coast of California.
Not all monarch populations make major migrations. Monarchs migrate short distances in Australia and New Zealand. There are some populations, for instance in Florida and the Caribbean, that do not migrate, as well as another subspecies distributed in the Caribbean, Central America and northern South America. Additional overwintering sites have been identified in Arizona and northern Florida.[1]
- ^ a b Morris, Gail M.; Klein, Christopher; Morris, Scott M. (2015). "Status of Danaus plexippus population in Arizona" (PDF). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society. 69 (2): 91–107. doi:10.18473/lepi.69i2.a10. S2CID 87653856.
- "Status of Danaus plexippus in Arizona" (PDF). Southwest Monarch Study.
- ^ Pyle 1981, pp. 712–713.
- ^ "The monarch super generation | U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Midwest Region". www.fws.gov. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
Previous Page Next Page


