Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Myotoxin
| Myotoxin | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
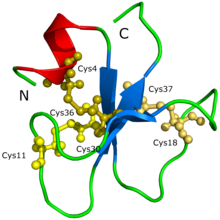 Structure of crotamine, a Na+ channel affecting toxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom.[1] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Myotoxins | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00819 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000881 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00435 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1h5o / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Myotoxins are small, basic peptides found in snake venoms (e.g. rattlesnakes)[2][3] and lizard venoms (e.g. Mexican beaded lizard).[4] This involves a non-enzymatic mechanism that leads to severe muscle necrosis. These peptides act very quickly, causing instantaneous paralysis to prevent prey from escaping and eventually death due to diaphragmatic paralysis.
The first myotoxin to be identified and isolated was crotamine, from the venom of Crotalus durissus terrificus, a tropical South American rattlesnake, by Brazilian scientist José Moura Gonçalves, in the 1950s. Its biological actions, molecular structure and gene responsible for its synthesis were all elucidated in the last two decades.
- ^ Nicastro G, Franzoni L, de Chiara C, Mancin AC, Giglio JR, Spisni A (May 2003). "Solution structure of crotamine, a Na+ channel affecting toxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom". Eur. J. Biochem. 270 (9): 1969–79. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03563.x. PMID 12709056.
- ^ Griffin PR, Aird SD (1990). "A new small myotoxin from the venom of the prairie rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis viridis)". FEBS Lett. 274 (1): 43–47. Bibcode:1990FEBSL.274...43G. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)81325-I. PMID 2253781. S2CID 45019479.
- ^ Samejima Y, Aoki Y, Mebs D (1991). "Amino acid sequence of a myotoxin from venom of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus)". Toxicon. 29 (4): 461–468. Bibcode:1991Txcn...29..461S. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(91)90020-r. PMID 1862521.
- ^ Whittington, CM; Papenfuss, AT; Bansal, P; Torres, AM; Wong, ES; Deakin, JE; Graves, T; Alsop, A; Schatzkamer, K; Kremitzki, C; Ponting, CP; Temple-Smith, P; Warren, WC; Kuchel, PW; Belov, K (Jun 2008). "Defensins and the convergent evolution of platypus and reptile venom genes". Genome Research. 18 (6): 986–94. doi:10.1101/gr.7149808. PMC 2413166. PMID 18463304.
Previous Page Next Page


