Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Norrland
Norrland | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates: 65°N 18°E / 65°N 18°E | |
| Area | |
• Total | 261,292 km2 (100,885 sq mi) |
| Population (31 December 2021)[1] | |
• Total | 1,188,031 |
| • Density | 4.5/km2 (12/sq mi) |
| Gross Regional Product | |
| • Total | SEK 427.062 billion €45.629 billion (2015) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |

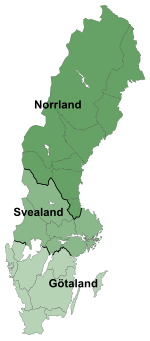

Norrland (Swedish: [ˈnɔ̌rːland] ⓘ, lit. 'Northland', originally Norrlanden, meaning 'the Northlands') is the northernmost, largest and least populated of the three traditional lands of Sweden, consisting of nine provinces. Although Norrland does not serve any administrative purposes, it continues to exist as a historical, cultural, and geographic region; it is often referred to in everyday language, e.g., in weather forecasts. Several related Norrland dialects form a distinct subset of dialects of the Swedish language separate from those to its south.
Norrland consists of the majority of the Swedish landmass at about 60% of the land area, but only has about 12% of the country's population.[3] Its largest city is Umeå, while the other four county seats are Gävle, Härnösand, Östersund and Luleå. The largest non-capitals are Sundsvall, Skellefteå and Örnsköldsvik while Kiruna is the largest town of the vast Lapland province in the far north. Sweden's highest mountain Kebnekaise and deepest lake of Hornavan are in Norrland. Plenty of long rivers originating in the mountains run through the Norrland forests, with major coastal towns frequently being on their estuaries. Their extensive drops in elevation also make Norrland a major producer of hydroelectricity from some of those rivers.
Winters in Norrland are cold by Swedish standards but mild for the latitudes. The vastness of the region renders very different environments and climates, ranging from mild coastal climates of Gävleborg to the tundra climate of the high mountains. In general, the most common climate is the subarctic type. The cold climate has led to winter sports being popular, with Norrland teams and athletes being especially successful in ice hockey, skiing and bandy.
- ^ "Folkmängd i landskapen den 31 december 2021" (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. Retrieved 2022-08-23.
- ^ Regions and Cities > Regional Statistics > Regional Economy > Regional GDP per Capita, OECD.Stats. Accessed on 16 November 2018.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Statistics Swedenwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page


