Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Phenyl group
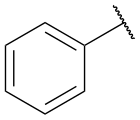
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph (archaically φ) or Ø. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry.[1] Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring.[1][2]
- ^ a b March, Jerry (1992). Advanced organic chemistry: reactions, mechanisms, and structure (4th ed.). New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-60180-7.
- ^ "Aromaticity. Benzene and Other Aromatic Compounds". Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry. Michigan State University.
Previous Page Next Page


