Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Philippines
Republic of the Philippines Republika ng Pilipinas (Filipino) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Maka-Diyos, Maka-tao, Makakalikasan at Makabansa[1] "For God, People, Nature, and Country" | |
| Anthem: "Lupang Hinirang" "Chosen Land" | |
| Capital | Manila (de jure) Metro Manila[b] (de facto) |
| Largest city | Quezon City |
| Official languages | |
| Recognized regional languages | 19 languages[4] |
National sign language | Filipino Sign Language |
Other recognized languages[c] | Spanish and Arabic |
| Ethnic groups (2020[6]) | |
| Religion (2020)[7] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Filipino (neutral) Filipina (feminine) Pinoy (adjective for certain common nouns) |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| Bongbong Marcos | |
| Sara Duterte | |
| Francis Escudero | |
| Martin Romualdez | |
| Alexander Gesmundo | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from Spain and the United States | |
| June 12, 1898 | |
• Cession | April 11, 1899 |
| November 15, 1935 | |
| July 4, 1946 | |
| February 2, 1987 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 300,000[8][9][e] km2 (120,000 sq mi) (72nd) |
• Water (%) | 0.61[10] (inland waters) |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | |
• 2020 census | |
• Density | 363.45/km2 (941.3/sq mi) (36th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2021) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (113th) |
| Currency | Philippine peso (₱) (PHP) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PhST) |
| Date format | MM/DD/YYYY DD/MM/YYYY[f] |
| Drives on | Right[16] |
| Calling code | +63 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH |
| Internet TLD | .ph |
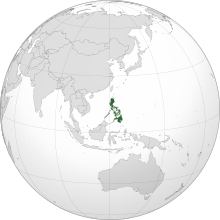
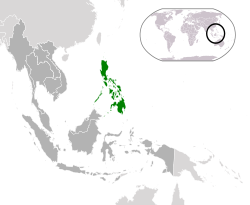
The Philippines,[g] officially the Republic of the Philippines,[h] is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. In the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It is the world's twelfth-most-populous country, with diverse ethnicities and cultures. Manila is the country's capital, and its most populated city is Quezon City. Both are within Metro Manila.
Negritos, the archipelago's earliest inhabitants, were followed by waves of Austronesian peoples. The adoption of animism, Hinduism with Buddhist influence, and Islam established island-kingdoms ruled by datus, rajas, and sultans. Extensive overseas trade with neighbors such as the late Tang or Song empire brought Chinese people to the archipelago as well, which would also gradually settle in and intermix over the centuries.
The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer leading a fleet for Castile, marked the beginning of Spanish colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of King Philip II of Castile. Spanish colonization via New Spain, beginning in 1565, led to the Philippines becoming ruled by the Crown of Castile, as part of the Spanish Empire, for more than 300 years. Catholic Christianity became the dominant religion, and Manila became the western hub of trans-Pacific trade. Hispanic immigrants from Latin America and Iberia would also selectively colonize. The Philippine Revolution began in 1896, and became entwined with the 1898 Spanish–American War. Spain ceded the territory to the United States, and Filipino revolutionaries declared the First Philippine Republic. The ensuing Philippine–American War ended with the United States controlling the territory until the Japanese invasion of the islands during World War II. After the United States retook the Philippines from the Japanese, the Philippines became independent in 1946. The country has had a tumultuous experience with democracy, which included the overthrow of a decades-long dictatorship in a nonviolent revolution.
The Philippines is an emerging market and a developing and newly industrialized country, whose economy is transitioning from being agricultural to service- and manufacturing-centered. It is a founding member of the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, ASEAN, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, and the East Asia Summit; it is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement and a major non-NATO ally of the United States. Its location as an island country on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes it prone to earthquakes and typhoons. The Philippines has a variety of natural resources and a globally-significant level of biodiversity.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Republic Act No. 8491 (February 12, 1998), Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines, Metro Manila, Philippines: Official Gazette of the Philippines, archived from the original on May 25, 2017, retrieved March 8, 2014
- ^ Presidential Decree No. 940, s. 1976 (May 29, 1976), Establishing Manila as the Capital of the Philippines and as the Permanent Seat of the National Government, Manila, Philippines: Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines, archived from the original on May 25, 2017, retrieved April 4, 2015
- ^ "Quezon City Local Government – Background". Quezon City Local Government. Archived from the original on August 20, 2020. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
GMA-DepEd-7-Languageswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
GovPH-OfficialLanguagewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Ethnicity in the Philippines (2020 Census of Population and Housing)". Philippine Statistics Authority (Press release). Archived from the original on September 6, 2023. Retrieved May 11, 2024.
- ^ a b Mapa, Dennis (February 21, 2023). "Religious Affiliation in the Philippines (2020 Census of Population and Housing)" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority (Press release). p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 12, 2023. Retrieved May 11, 2024.
- ^ "Philippines country profile". BBC News. December 19, 2023. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved January 10, 2024.
- ^ "Philippines". Central Intelligence Agency. February 27, 2023. Archived from the original on January 10, 2021. Retrieved February 24, 2023 – via CIA.gov.
- ^ "Philippines". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. June 7, 2023. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- ^ "Population Projection Statistics". psa.gov.ph. March 28, 2021. Archived from the original on December 26, 2023. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- ^ Mapa, Dennis S. (July 7, 2021). "2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH) Population Counts Declared Official by the President" (Press release). Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2024 Edition. (Philippines)". International Monetary Fund. April 16, 2024. Archived from the original on April 16, 2024. Retrieved April 17, 2024.
- ^ "Highlights of the Preliminary Results of the 2021 Annual Family Income and Expenditure Survey" (Press release). PSA. Archived from the original on May 16, 2023. Retrieved August 15, 2022.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. March 13, 2024. p. 289. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 13, 2024. Retrieved March 13, 2024.
- ^ Philippine Yearbook (1978 ed.). Manila, Philippines: National Economic and Development Authority, National Census and Statistics Office. 1978. p. 716. Archived from the original on March 6, 2023. Retrieved February 18, 2023.
Previous Page Next Page


![Coat of arms[a] of the Philippines](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/84/Coat_of_arms_of_the_Philippines.svg/85px-Coat_of_arms_of_the_Philippines.svg.png)