Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Polydimethylsiloxane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
poly(dimethylsiloxane)
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.442 |
| E number | E900 (glazing agents, ...) |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
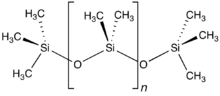
| CH3[Si(CH3)2O]nSi(CH3)3 | |
| Density | 0.965 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | N/A, vitrifies |
| Boiling point | N/A, vitrifies |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03AX05 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication and passive daytime radiative cooling.[1][2][3]
PDMS is particularly known for its unusual rheological (or flow) properties. It is optically clear and, in general, inert, non-toxic, and non-flammable. It is one of several types of silicone oil (polymerized siloxane). The applications of PDMS range from contact lenses and medical devices to elastomers; it is also present in shampoos (as it makes hair shiny and slippery), food (antifoaming agent), caulk, lubricants and heat-resistant tiles.
- ^ Simsek, Eylul; Mandal, Jyotirmoy; Raman, Aaswath P.; Pilon, Laurent (December 2022). "Dropwise condensation reduces selectivity of sky-facing radiative cooling surfaces". International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer. 198: 123399. Bibcode:2022IJHMT.19823399S. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.123399. S2CID 252242911.
- ^ "Linear Polydimethylsiloxanes". ECETOC (second ed.). 2011-12-28.
- ^ Wolf, Marc P.; Salieb-Beugelaar, Georgette B.; Hunziker, Patrick (2018). "PDMS with designer functionalities—Properties, modifications strategies, and applications". Progress in Polymer Science. 83. Elsevier BV: 97–134. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.06.001. ISSN 0079-6700. S2CID 102916647.
Previous Page Next Page





