Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Internet
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the internetwork. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected articleRed vs. Blue is a science fiction comedy series created by Rooster Teeth Productions. The series is produced primarily by using the machinima technique of synchronizing video footage from computer and video games to pre-recorded dialogue and other audio. Footage is taken mostly from the multiplayer modes of the first-person shooter (FPS) video games Halo: Combat Evolved and Halo 2 on the Xbox video game console. Chronicling the story of two opposing teams of soldiers fighting a civil war in the middle of a desolate box canyon, the series is an absurdist parody of FPS games, military life, and other science fiction films. Begun in 2003 and having concluded its fourth season, Red vs. Blue has won four awards from the Academy of Machinima Arts & Sciences. The series is generally praised for its originality, and has been credited with bringing new popularity to machinima, helping it to gain more mainstream exposure, and attracting more people to the art form. Selected picture A hotspot is a venue that offers Wi-Fi access. The public can use a laptop, WiFi phone, or other suitable portable device to access the Internet. Of the estimated 150 million laptops, 14 million PDAs, and other emerging Wi-Fi devices sold per year for the last few years, most include the Wi-Fi feature. Ralph Breaks the Internet is a 2018 American animated comedy film produced by Walt Disney Animation Studios and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It is the sequel to the 2012 film Wreck-It Ralph. The film was directed by Rich Moore and Phil Johnston, and produced by Clark Spencer, from a screenplay written by Johnston and Pamela Ribon, and a story by Moore, Johnston, Ribon, Josie Trinidad, and Jim Reardon. John Lasseter, Jennifer Lee, and Chris Williams served as the film's executive producers. John C. Reilly, Sarah Silverman, Jack McBrayer, Jane Lynch, and Ed O'Neill reprise their character roles from the first film, and are joined by Gal Gadot, Taraji P. Henson, and Alfred Molina as part of the new cast, as well as Alan Tudyk, who voiced a new character in this film. In the film, Ralph (Reilly) and Vanellope von Schweetz (Silverman) must travel to the Internet to get a replacement for the Sugar Rush cabinet's broken steering wheel and prevent Mr. Litwak (O'Neill) from disposing of the game. The first discussions about a sequel to Wreck-It Ralph began in September 2012, and the new installment went through three different scripts before the filmmakers settled on the final plot. When the film was officially announced in June 2016 as Ralph Breaks the Internet: Wreck-It Ralph 2, much of the original cast confirmed they had signed on, with new cast members added in 2018. It is Walt Disney Animation Studios' first computer-animated film sequel and is the first sequel from the studio to be created by the original film's creative team. Ralph Breaks the Internet premiered in Hollywood, Los Angeles, on November 5, 2018, and was released in the United States on November 21. The film grossed over $529.3 million worldwide against its $175 million budget and received generally positive reviews from critics. The film was nominated for Best Animated Feature at the 91st Academy Awards, 76th Golden Globe Awards, 46th Annie Awards, and 24th Critics' Choice Awards, losing all four awards to Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse. (Full article...) WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Sergey Brin (Russian: Сергей Михайлович Брин; born August 21, 1973) is a Russian-born American entrepreneur who co-founded Google with Larry Page. Brin currently holds the position of President of Technology at Google and has a net worth estimated at $18.5 billion as of March 9, 2007, making him the 26th richest person in the world and the 5th richest person in the United States, together with Larry Page. He is also the fourth-youngest billionaire in the world. After graduating from the University of Maryland, Brin received a graduate fellowship from the National Science Foundation, which allowed him to study for his master's degree in computer science at Stanford University. Brin received his master's degree in August 1995 ahead of schedule in the process of his Ph.D. studies. Although he is still enrolled in the Stanford doctoral program, Brin has suspended his Ph.D. studies indefinitely while he is working at Google. Brin met Larry Page while they were both graduate students at Stanford, and they authored a paper together entitled a paper entitled "The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine."
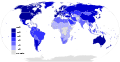
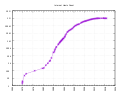
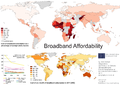
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMain topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |
Previous Page Next Page