Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Mathematics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Wikipedia portal for content related to Mathematics
-
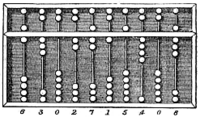
Abacus, a ancient hand-operated calculating.
-
Portrait of Emmy Noether, around 1900.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). (Full article...)
Featured articles
-
Image 1

The manipulations of the Rubik's Cube form the Rubik's Cube group.
In mathematics, a group is a set with an operation that associates every pair of elements of the set to an element of the set (as does every binary operation) and satisfies the following constraints: the operation is associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element.
Many mathematical structures are groups endowed with other properties. For example, the integers with the addition operation form an infinite group, which is generated by a single element called (these properties characterize the integers in a unique way). (Full article...)
-
Image 2In classical mechanics, the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector (LRL vector) is a vector used chiefly to describe the shape and orientation of the orbit of one astronomical body around another, such as a binary star or a planet revolving around a star. For two bodies interacting by Newtonian gravity, the LRL vector is a constant of motion, meaning that it is the same no matter where it is calculated on the orbit; equivalently, the LRL vector is said to be conserved. More generally, the LRL vector is conserved in all problems in which two bodies interact by a central force that varies as the inverse square of the distance between them; such problems are called Kepler problems.
The hydrogen atom is a Kepler problem, since it comprises two charged particles interacting by Coulomb's law of electrostatics, another inverse-square central force. The LRL vector was essential in the first quantum mechanical derivation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom, before the development of the Schrödinger equation. However, this approach is rarely used today. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The weighing pans of this balance scale contain zero objects, divided into two equal groups.
In mathematics, zero is an even number. In other words, its parity—the quality of an integer being even or odd—is even. This can be easily verified based on the definition of "even": zero is an integer multiple of 2, specifically 0 × 2. As a result, zero shares all the properties that characterize even numbers: for example, 0 is neighbored on both sides by odd numbers, any decimal integer has the same parity as its last digit—so, since 10 is even, 0 will be even, and if y is even then y + x has the same parity as x—indeed, 0 + x and x always have the same parity.
Zero also fits into the patterns formed by other even numbers. The parity rules of arithmetic, such as even − even = even, require 0 to be even. Zero is the additive identity element of the group of even integers, and it is the starting case from which other even natural numbers are recursively defined. Applications of this recursion from graph theory to computational geometry rely on zero being even. Not only is 0 divisible by 2, it is divisible by every power of 2, which is relevant to the binary numeral system used by computers. In this sense, 0 is the "most even" number of all. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Edward Wright (baptised 8 October 1561; died November 1615) was an English mathematician and cartographer noted for his book Certaine Errors in Navigation (1599; 2nd ed., 1610), which for the first time explained the mathematical basis of the Mercator projection by building on the works of Pedro Nunes, and set out a reference table giving the linear scale multiplication factor as a function of latitude, calculated for each minute of arc up to a latitude of 75°. This was in fact a table of values of the integral of the secant function, and was the essential step needed to make practical both the making and the navigational use of Mercator charts.
Wright was born at Garveston in Norfolk and educated at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, where he became a fellow from 1587 to 1596. In 1589 the college granted him leave after Elizabeth I requested that he carry out navigational studies with a raiding expedition organised by the Earl of Cumberland to the Azores to capture Spanish galleons. The expedition's route was the subject of the first map to be prepared according to Wright's projection, which was published in Certaine Errors in 1599. The same year, Wright created and published the first world map produced in England and the first to use the Mercator projection since Gerardus Mercator's original 1569 map. (Full article...) -
Image 5
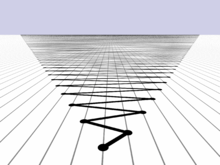
The first 15,000 partial sums of 0 + 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ... The graph is situated with positive integers to the right and negative integers to the left.
In mathematics, 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ··· is an infinite series whose terms are the successive positive integers, given alternating signs. Using sigma summation notation the sum of the first m terms of the series can be expressed as
The infinite series diverges, meaning that its sequence of partial sums, (1, −1, 2, −2, 3, ...), does not tend towards any finite limit. Nonetheless, in the mid-18th century, Leonhard Euler wrote what he admitted to be a paradoxical equation:(Full article...)
-
Image 6Elementary algebra studies which values solve equations formed using arithmetical operations.
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that studies certain abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic operations other than the standard arithmetic operations, such as addition and multiplication.
Elementary algebra is the main form of algebra taught in schools. It examines mathematical statements using variables for unspecified values and seeks to determine for which values the statements are true. To do so, it uses different methods of transforming equations to isolate variables. Linear algebra is a closely related field that investigates linear equations and combinations of them called systems of linear equations. It provides methods to find the values that solve all equations in the system at the same time, and to study the set of these solutions. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Émile Michel Hyacinthe Lemoine (French: [emil ləmwan]; 22 November 1840 – 21 February 1912) was a French civil engineer and a mathematician, a geometer in particular. He was educated at a variety of institutions, including the Prytanée National Militaire and, most notably, the École Polytechnique. Lemoine taught as a private tutor for a short period after his graduation from the latter school.
Lemoine is best known for his proof of the existence of the Lemoine point (or the symmedian point) of a triangle. Other mathematical work includes a system he called Géométrographie and a method which related algebraic expressions to geometric objects. He has been called a co-founder of modern triangle geometry, as many of its characteristics are present in his work. (Full article...) -
Image 8
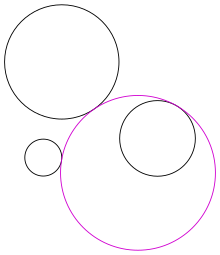
Figure 1: A solution (in purple) to Apollonius's problem. The given circles are shown in black.
In Euclidean plane geometry, Apollonius's problem is to construct circles that are tangent to three given circles in a plane (Figure 1). Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 BC – c. 190 BC) posed and solved this famous problem in his work Ἐπαφαί (Epaphaí, "Tangencies"); this work has been lost, but a 4th-century AD report of his results by Pappus of Alexandria has survived. Three given circles generically have eight different circles that are tangent to them (Figure 2), a pair of solutions for each way to divide the three given circles in two subsets (there are 4 ways to divide a set of cardinality 3 in 2 parts).
In the 16th century, Adriaan van Roomen solved the problem using intersecting hyperbolas, but this solution does not use only straightedge and compass constructions. François Viète found such a solution by exploiting limiting cases: any of the three given circles can be shrunk to zero radius (a point) or expanded to infinite radius (a line). Viète's approach, which uses simpler limiting cases to solve more complicated ones, is considered a plausible reconstruction of Apollonius' method. The method of van Roomen was simplified by Isaac Newton, who showed that Apollonius' problem is equivalent to finding a position from the differences of its distances to three known points. This has applications in navigation and positioning systems such as LORAN. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Logic studies valid forms of inference like modus ponens.
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.
Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to work". Premises and conclusions express propositions or claims that can be true or false. An important feature of propositions is their internal structure. For example, complex propositions are made up of simpler propositions linked by logical vocabulary like(and) or
(if...then). Simple propositions also have parts, like "Sunday" or "work" in the example. The truth of a proposition usually depends on the meanings of all of its parts. However, this is not the case for logically true propositions. They are true only because of their logical structure independent of the specific meanings of the individual parts. (Full article...)
-
Image 10Archimedes Thoughtful by Fetti (1620)
Archimedes of Syracuse (/ˌɑːrkɪˈmiːdiːz/ AR-kim-EE-deez; c. 287 – c. 212 BC) was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Regarded as the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time, Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral.
Archimedes' other mathematical achievements include deriving an approximation of pi (π), defining and investigating the Archimedean spiral, and devising a system using exponentiation for expressing very large numbers. He was also one of the first to apply mathematics to physical phenomena, working on statics and hydrostatics. Archimedes' achievements in this area include a proof of the law of the lever, the widespread use of the concept of center of gravity, and the enunciation of the law of buoyancy known as Archimedes' principle. In astronomy, he made measurements of the apparent diameter of the Sun and the size of the universe. He is also credited with designing innovative machines, such as his screw pump, compound pulleys, and defensive war machines to protect his native Syracuse from invasion. (Full article...) -
Image 11

High-precision test of general relativity by the Cassini space probe (artist's impression): radio signals sent between the Earth and the probe (green wave) are delayed by the warping of spacetime (blue lines) due to the Sun's mass.
General relativity is a theory of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. The theory of general relativity says that the observed gravitational effect between masses results from their warping of spacetime.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Newton's law of universal gravitation had been accepted for more than two hundred years as a valid description of the gravitational force between masses. In Newton's model, gravity is the result of an attractive force between massive objects. Although even Newton was troubled by the unknown nature of that force, the basic framework was extremely successful at describing motion. (Full article...) -
Image 12In algebraic geometry and theoretical physics, mirror symmetry is a relationship between geometric objects called Calabi–Yau manifolds. The term refers to a situation where two Calabi–Yau manifolds look very different geometrically but are nevertheless equivalent when employed as extra dimensions of string theory.
Early cases of mirror symmetry were discovered by physicists. Mathematicians became interested in this relationship around 1990 when Philip Candelas, Xenia de la Ossa, Paul Green, and Linda Parkes showed that it could be used as a tool in enumerative geometry, a branch of mathematics concerned with counting the number of solutions to geometric questions. Candelas and his collaborators showed that mirror symmetry could be used to count rational curves on a Calabi–Yau manifold, thus solving a longstanding problem. Although the original approach to mirror symmetry was based on physical ideas that were not understood in a mathematically precise way, some of its mathematical predictions have since been proven rigorously. (Full article...) -
Image 13Damage from Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Actuaries need to estimate long-term levels of such damage in order to accurately price property insurance, set appropriate reserves, and design appropriate reinsurance and capital management strategies.
An actuary is a professional with advanced mathematical skills who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require asset management, liability management, and valuation skills. Actuaries provide assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms. The name of the corresponding academic discipline is actuarial science.
While the concept of insurance dates to antiquity, the concepts needed to scientifically measure and mitigate risks have their origins in the 17th century studies of probability and annuities. Actuaries of the 21st century require analytical skills, business knowledge, and an understanding of human behavior and information systems to design programs that manage risk, by determining if the implementation of strategies proposed for mitigating potential risks, does not exceed the expected cost of those risks actualized. The steps needed to become an actuary, including education and licensing, are specific to a given country, with various additional requirements applied by regional administrative units; however, almost all processes impart universal principles of risk assessment, statistical analysis, and risk mitigation, involving rigorously structured training and examination schedules, taking many years to complete. (Full article...) -
Image 14A stamp of Zhang Heng issued by China Post in 1955
Zhang Heng (Chinese: 張衡; AD 78–139), formerly romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mathematician, seismologist, hydraulic engineer, inventor, geographer, cartographer, ethnographer, artist, poet, philosopher, politician, and literary scholar.
Zhang Heng began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stance on historical and calendrical issues led to his becoming a controversial figure, preventing him from rising to the status of Grand Historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian Kingdom in present-day Hebei. Zhang returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Theodore John Kaczynski (/kəˈzɪnski/ ⓘ kə-ZIN-skee; May 22, 1942 – June 10, 2023), also known as the Unabomber (/ˈjuːnəbɒmər/ ⓘ YOO-nə-bom-ər), was an American mathematician and domestic terrorist. He was a mathematics prodigy, but abandoned his academic career in 1969 to pursue a reclusive primitive lifestyle.
Kaczynski murdered three people and injured 23 others between 1978 and 1995 in a nationwide mail bombing campaign against people he believed to be advancing modern technology and the destruction of the natural environment. He authored Industrial Society and Its Future, a 35,000-word manifesto and social critique opposing all forms of technology, rejecting leftism, and advocating a nature-centered form of anarchism. (Full article...)
Good articles
-
Image 1

The boundary of a Reuleaux triangle is a constant width curve based on an equilateral triangle. All points on a side are equidistant from the opposite vertex.
A Reuleaux triangle [ʁœlo] is a curved triangle with constant width, the simplest and best known curve of constant width other than the circle. It is formed from the intersection of three circular disks, each having its center on the boundary of the other two. Constant width means that the separation of every two parallel supporting lines is the same, independent of their orientation. Because its width is constant, the Reuleaux triangle is one answer to the question "Other than a circle, what shape can a manhole cover be made so that it cannot fall down through the hole?"
They are named after Franz Reuleaux, a 19th-century German engineer who pioneered the study of machines for translating one type of motion into another, and who used Reuleaux triangles in his designs. However, these shapes were known before his time, for instance by the designers of Gothic church windows, by Leonardo da Vinci, who used it for a map projection, and by Leonhard Euler in his study of constant-width shapes. Other applications of the Reuleaux triangle include giving the shape to guitar picks, fire hydrant nuts, pencils, and drill bits for drilling filleted square holes, as well as in graphic design in the shapes of some signs and corporate logos. (Full article...) -
Image 2

A convex curve (black) forms a connected subset of the boundary of a convex set (blue), and has a supporting line (red) through each of its points.
In geometry, a convex curve is a plane curve that has a supporting line through each of its points. There are many other equivalent definitions of these curves, going back to Archimedes. Examples of convex curves include the convex polygons, the boundaries of convex sets, and the graphs of convex functions. Important subclasses of convex curves include the closed convex curves (the boundaries of bounded convex sets), the smooth curves that are convex, and the strictly convex curves, which have the additional property that each supporting line passes through a unique point of the curve.
Bounded convex curves have a well-defined length, which can be obtained by approximating them with polygons, or from the average length of their projections onto a line. The maximum number of grid points that can belong to a single curve is controlled by its length. The points at which a convex curve has a unique supporting line are dense within the curve, and the distance of these lines from the origin defines a continuous support function. A smooth simple closed curve is convex if and only if its curvature has a consistent sign, which happens if and only if its total curvature equals its total absolute curvature. (Full article...) -
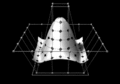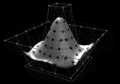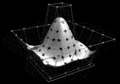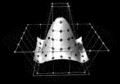
Image 3
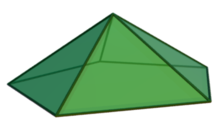
In geometry, a pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a pentagon base and five triangular faces, having a total of six faces. It is categorized as a Johnson solid if all of the edges are equal in length, forming equilateral triangular faces and a regular pentagonal base.
Pentagonal pyramids occur as pieces and tools in the construction of many polyhedra. They also appear in the field of natural science, as in stereochemistry where the shape can be described as the pentagonal pyramidal molecular geometry, as well as the study of shell assembling in the underlying potential energy surfaces and disclination in fivelings and related shapes such as pyramidal copper and other metal nanowires. (Full article...) -
Image 4
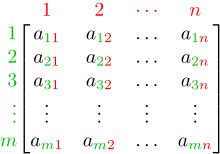
An m × n matrix: the m rows are horizontal and the n columns are vertical. Each element of a matrix is often denoted by a variable with two subscripts. For example, a2,1 represents the element at the second row and first column of the matrix.
In mathematics, a matrix (pl.: matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object.
For example,
is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a "matrix", or a matrix of dimension
. (Full article...)
-
Image 5

The graph of the 3-3 duoprism (the line graph of ) is perfect. Here it is colored with three colors, with one of its 3-vertex maximum cliques highlighted.
In graph theory, a perfect graph is a graph in which the chromatic number equals the size of the maximum clique, both in the graph itself and in every induced subgraph. In all graphs, the chromatic number is greater than or equal to the size of the maximum clique, but they can be far apart. A graph is perfect when these numbers are equal, and remain equal after the deletion of arbitrary subsets of vertices.
The perfect graphs include many important families of graphs and serve to unify results relating colorings and cliques in those families. For instance, in all perfect graphs, the graph coloring problem, maximum clique problem, and maximum independent set problem can all be solved in polynomial time, despite their greater complexity for non-perfect graphs. In addition, several important minimax theorems in combinatorics, including Dilworth's theorem and Mirsky's theorem on partially ordered sets, Kőnig's theorem on matchings, and the Erdős–Szekeres theorem on monotonic sequences, can be expressed in terms of the perfection of certain associated graphs. (Full article...) -
Image 6In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative integer
, denoted by
, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to
. The factorial of
also equals the product of
with the next smaller factorial:
For example,
The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product.
Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book Sefer Yetzirah. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – ofdistinct objects: there are
. In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the exponential function and other functions, and they also have applications in algebra, number theory, probability theory, and computer science. (Full article...)
-
Image 7

A unit distance graph with 16 vertices and 40 edges
In mathematics, particularly geometric graph theory, a unit distance graph is a graph formed from a collection of points in the Euclidean plane by connecting two points whenever the distance between them is exactly one. To distinguish these graphs from a broader definition that allows some non-adjacent pairs of vertices to be at distance one, they may also be called strict unit distance graphs or faithful unit distance graphs. As a hereditary family of graphs, they can be characterized by forbidden induced subgraphs. The unit distance graphs include the cactus graphs, the matchstick graphs and penny graphs, and the hypercube graphs. The generalized Petersen graphs are non-strict unit distance graphs.
An unsolved problem of Paul Erdős asks how many edges a unit distance graph onvertices can have. The best known lower bound is slightly above linear in
—far from the upper bound, proportional to
. The number of colors required to color unit distance graphs is also unknown (the Hadwiger–Nelson problem): some unit distance graphs require five colors, and every unit distance graph can be colored with seven colors. For every algebraic number there is a unit distance graph with two vertices that must be that distance apart. According to the Beckman–Quarles theorem, the only plane transformations that preserve all unit distance graphs are the isometries. (Full article...)
-
Image 8

A polyhedron and its midsphere. The red circles are the boundaries of spherical caps within which the surface of the sphere can be seen from each vertex.
In geometry, the midsphere or intersphere of a convex polyhedron is a sphere which is tangent to every edge of the polyhedron. Not every polyhedron has a midsphere, but the uniform polyhedra, including the regular, quasiregular and semiregular polyhedra and their duals (Catalan solids) all have midspheres. The radius of the midsphere is called the midradius. A polyhedron that has a midsphere is said to be midscribed about this sphere.
When a polyhedron has a midsphere, one can form two perpendicular circle packings on the midsphere, one corresponding to the adjacencies between vertices of the polyhedron, and the other corresponding in the same way to its polar polyhedron, which has the same midsphere. The length of each polyhedron edge is the sum of the distances from its two endpoints to their corresponding circles in this circle packing. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Hugo Dyonizy Steinhaus (English: /ˈhjuːɡoʊ ˈstaɪnhaʊs/ HEW-goh STYNE-howss, Polish: [ˈxuɡɔ ˈʂtajnxaws], German: [ˈhuːɡoː ˈʃtaɪnhaʊs]; 14 January 1887 – 25 February 1972) was a Polish mathematician and educator. Steinhaus obtained his PhD under David Hilbert at Göttingen University in 1911 and later became a professor at the Jan Kazimierz University in Lwów (now Lviv, Ukraine), where he helped establish what later became known as the Lwów School of Mathematics. He is credited with "discovering" mathematician Stefan Banach, with whom he gave a notable contribution to functional analysis through the Banach–Steinhaus theorem. After World War II Steinhaus played an important part in the establishment of the mathematics department at Wrocław University and in the revival of Polish mathematics from the destruction of the war.
Author of around 170 scientific articles and books, Steinhaus has left his legacy and contribution in many branches of mathematics, such as functional analysis, geometry, mathematical logic, and trigonometry. Notably he is regarded as one of the early founders of game theory and probability theory, which led to later development of more comprehensive approaches by other scholars. (Full article...) -
Image 10
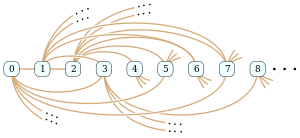
The Rado graph, as numbered by Ackermann (1937) harvtxt error: no target: CITEREFAckermann1937 (help) and Rado (1964) harvtxt error: no target: CITEREFRado1964 (help).
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Rado graph, Erdős–Rényi graph, or random graph is a countably infinite graph that can be constructed (with probability one) by choosing independently at random for each pair of its vertices whether to connect the vertices by an edge. The names of this graph honor Richard Rado, Paul Erdős, and Alfréd Rényi, mathematicians who studied it in the early 1960s; it appears even earlier in the work of Wilhelm Ackermann (1937). The Rado graph can also be constructed non-randomly, by symmetrizing the membership relation of the hereditarily finite sets, by applying the BIT predicate to the binary representations of the natural numbers, or as an infinite Paley graph that has edges connecting pairs of prime numbers congruent to 1 mod 4 that are quadratic residues modulo each other.
Every finite or countably infinite graph is an induced subgraph of the Rado graph, and can be found as an induced subgraph by a greedy algorithm that builds up the subgraph one vertex at a time. The Rado graph is uniquely defined, among countable graphs, by an extension property that guarantees the correctness of this algorithm: no matter which vertices have already been chosen to form part of the induced subgraph, and no matter what pattern of adjacencies is needed to extend the subgraph by one more vertex, there will always exist another vertex with that pattern of adjacencies that the greedy algorithm can choose. (Full article...) -
Image 1169 (sixty-nine; LXIX) is the natural number following 68 and preceding 70. An odd number and a composite number, 69 is divisible by 1, 3, 23 and 69.
The number and its pictograph give its name to the sexual position of the same name. The association of the number with this sex position has resulted in it being associated in meme culture with sex. People knowledgeable of the meme may respond "nice" in response to the appearance of the number, whether intentionally an innuendo or not. (Full article...) -
Image 12The Erdős–Straus conjecture is an unproven statement in number theory. The conjecture is that, for every integer
that is greater than or equal to 2, there exist positive integers
,
, and
for which
In other words, the numbercan be written as a sum of three positive unit fractions.
The conjecture is named after Paul Erdős and Ernst G. Straus, who formulated it in 1948, but it is connected to much more ancient mathematics; sums of unit fractions, like the one in this problem, are known as Egyptian fractions, because of their use in ancient Egyptian mathematics. The Erdős–Straus conjecture is one of many conjectures by Erdős, and one of many unsolved problems in mathematics concerning Diophantine equations. (Full article...)
Did you know
- ... that Green Day's "Wake Me Up When September Ends" became closely associated with the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that owner Matthew Benham influenced both Brentford FC in the UK and FC Midtjylland in Denmark to use mathematical modelling to recruit undervalued football players?
- ... that in 1940 Xu Ruiyun became the first Chinese woman to receive a PhD in mathematics?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that despite published scholarship to the contrary, Andrew Planta neither received a doctorate nor taught mathematics at Erlangen?

- ...that the set of rational numbers is equal in size to the set of integers; that is, they can be put in one-to-one correspondence?
- ...that there are precisely six convex regular polytopes in four dimensions? These are analogs of the five Platonic solids known to the ancient Greeks.
- ...that it is unknown whether π and e are algebraically independent?
- ...that a nonconvex polygon with three convex vertices is called a pseudotriangle?
- ...that it is possible for a three-dimensional figure to have a finite volume but infinite surface area, such as Gabriel's Horn?
- ... that as the dimension of a hypersphere tends to infinity, its "volume" (content) tends to 0?
- ...that the primality of a number can be determined using only a single division using Wilson's Theorem?
Showing 7 items out of 75
Featured pictures
-
Image 1Mandelbrot set, step 3, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 2Mandelbrot set, step 4, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 4Mandelbrot set, step 13, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 5Mandelbrot set, step 7, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 6Fields Medal, front, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 7Mandelbrot set, start, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 8Desargues' theorem, by Dynablast (edited by Jujutacular and Julia W) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 9Mandelbrot set, step 6, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 10Proof of the Pythagorean theorem, by Joaquim Alves Gaspar (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 11Mandelbrot set, step 9, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 13Lorenz attractor at Chaos theory, by Wikimol (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 14Mandelbrot set, step 10, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 16Mandelbrot set, by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 17Cellular automata at Reflector (cellular automaton), by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 18Mandelbrot set, step 11, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
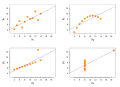
Image 19Anscombe's quartet, by Schutz (edited by Avenue) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 20Fields Medal, back, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 23Mandelbrot set, step 2, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 24Hypotrochoid, by Sam Derbyshire (edited by Anevrisme and Perhelion) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 25Non-uniform rational B-spline, by Greg L (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 26Mandelbrot set, step 8, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 27Tetrahedral group at Symmetry group, by Debivort (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 29Mandelbrot set, step 14, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 30Mandelbrot set, step 5, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 31Mandelbrot set, step 1, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 32Mandelbrot set, step 12, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 34Line integral of scalar field, by Lucas V. Barbosa (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
Get involved
- For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Mathematics-related articles, visit WikiProject Mathematics.
Categories
Topics
Index of articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Vital articles
- » subpages: Level 4 Mathematics articles, Level 5 Mathematics articles
Discover Wikipedia using portals
Previous Page Next Page